2016, 14(2) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第14卷 第2期
A zonal decoupling algorithm used to control a dual deformable mirror (DM) is proposed. One of the two DMs is characterized with a large stroke (woofer), while the other one is characterized by a high spatial frequency (tweeter). A numerical model is used to compare the zonal decoupling algorithm with some traditional zonal decoupling algorithms. The simulation results indicate that the algorithm presented in this Letter improves the performance in suppressing the coupling error. An experimental system is built to prove the effectiveness of this algorithm. The experiments demonstrate that the phase aberrations could be effectively compensated and that the coupling error could also be suppressed.
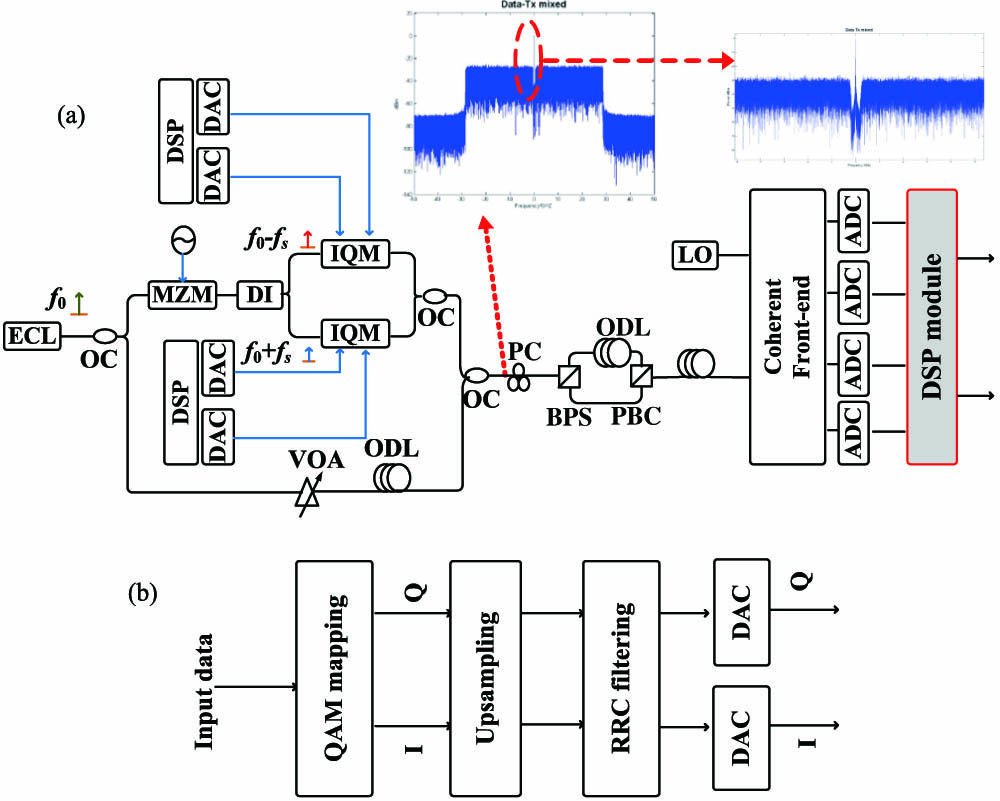
010.1080 Active or adoptive optics 220.1080 Active or adoptive optics 000.3860 Mathematical methods in physics A new two-stage carrier-phase recovery scheme using a combination of an optical pilot-aided algorithm with the crossed constellation transformation algorithm for either square-framed or non-square-framed M-level-quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) Nyquist systems is proposed. It is verified in 32- and 128-QAM systems that it can provide high linewidth tolerance with little complexity.
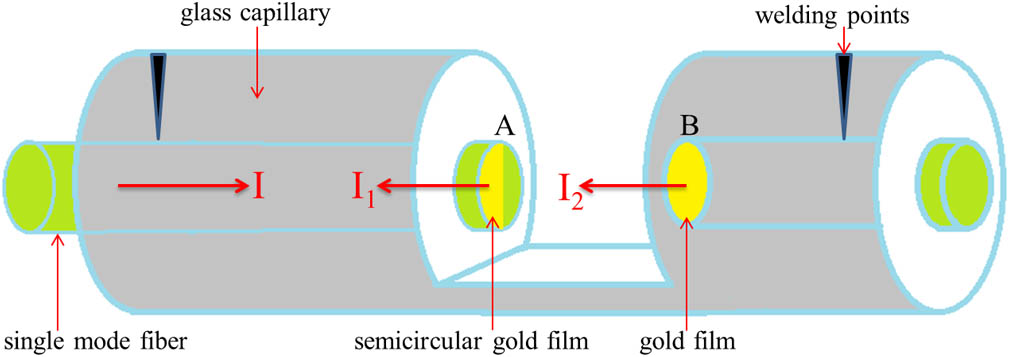
060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications 060.1660 Coherent communications 060.2330 Fiber optics communications An optical fiber extrinsic Fabry–Perot interferometer (EFPI) is designed and fabricated for refractive index (RI) sensing. To test the RI of liquid, the following two different methods are adopted: the wavelength tracking method and the Fourier-transform white-light interferometry (FTWLI). The sensitivities of sensors with cavity lengths of 288.1 and 358.5 μm are 702.312 nm/RIU and 396.362 μm/RIU, respectively, by the two methods. Our work provides a new kind of RI sensor with the advantages of high sensitivity, mechanical robustness, and low cross sensitivity to temperature. Also, we provide a new method to deal with gold film with a femtosecond laser.
060.2280 Fiber design and fabrication 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors Investigating the light stability of solid-solution-based AgCl-AgBr and AgBr-TlI crystals Download:986次
Download:986次
 Download:986次
Download:986次For the development of mid-infrared fiber-optical elements, one needs light-stable, flexible materials that are transparent within this spectral band. Solid solutions of silver and monadic thallium halides prove to be the most suitable crystalline media for these needs. We study the light stability variation of high-purity AgCl 1 x Br x 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 Ag 1 x Tl x Br 1 x I x 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.05 6500 350 cm 1
060.2290 Fiber materials 060.2390 Fiber optics, infrared 160.4670 Optical materials 160.4760 Optical properties Streak tube imaging lidar (STIL) is an active imaging system that has a high range accuracy with the use of a pulsed laser transmitter and streak tube receiver to produce 3D range images. This work investigates the effect of the time bin size on the range accuracy of STIL systems based on the peak detection algorithm. The numerical simulation indicates that the time bin size has a significant effect on the range accuracy, resulting in a modified analytical estimate of the range error. An indoor experiment with a planar target is carried out to validate the theory that shows the linear relationship between the range error and the time bin size. Finer 3D depth images of a fist model are acquired by using a smaller time bin size and the best range error of 0.003 m is achieved with the optimal time bin size of 0.07 ns.
110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition 280.3640 Lidar 150.5670 Range finding 280.4788 Optical sensing and sensors Based on a single-channel laser self-mixing interferometer, we present a new simultaneous measurement of the vibration amplitude and the rotation angle of objects that both affect the power spectrum containing two peaks of the interferometer signals. The fitted results indicate that the curve of the peak frequency versus the vibration amplitude follows a linear distribution, and the curve of the difference of the two-peak power values versus the angle follows a Gaussian distribution. A vibration amplitude with an error less than 3.0% and a rotation angle with an error less than 11.7% are calculated from the fitted results.
120.3180 Interferometry 140.3490 Lasers, distributed-feedback 140.3570 Lasers, single-mode A system of an add-drop microring resonator integrated with a sampled grating distributed feedback (SG-DFB) is investigated via modeling and simulation with the time-domain traveling wave (TDTW) method. The proposed microring resonator comprises a SiO 2 SiO 2 4.5 × 10 18 m 2 / W Q λ 0 1.93 × 10 5 2.87 × 10 5
130.3130 Integrated optics materials 130.3990 Micro-optical devices 130.7408 Wavelength filtering devices 050.2770 Gratings Polarization switching (PS) characteristics in a 1550 nm vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) subject to circularly polarized optical injection (CPOI) are experimentally investigated. The results show that, under different biased current, a solitary 1550 nm VCSEL can oscillate at y y x x y x
140.7260 Vertical cavity surface emitting lasers 190.3100 Instabilities and chaos 190.4360 Nonlinear optics, devices It is demonstrated that high-Q Q ~ 10 8 CO 2
140.4780 Optical resonators 140.3948 Microcavity devices A laser diode array side-pumped Nd:glass square rod amplifier of the dimensions 12 mm × 12 mm 10 mm × 10 mm
140.3480 Lasers, diode-pumped 140.5560 Pumping 140.2010 Diode laser arrays 140.0140 Lasers and laser optics Multiwavelength visible laser based on the stimulated Raman scattering effect and beta barium borate angle tuning Download:878次
Download:878次
 Download:878次
Download:878次We demonstrate wavelength-selectable visible emissions from a miniature crystalline laser that combines the stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) effect in an Nd : YVO 4
140.3550 Lasers, Raman 190.2620 Harmonic generation and mixing 140.3380 Laser materials The continuous wave (CW) and passively Q Nd : ( La x Gd 1 x ) 3 Gd 5 O 12 V 3 + : YAG
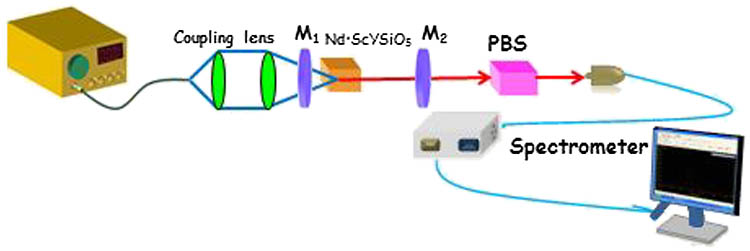
140.3530 Lasers, neodymium 320.5550 Pulses Anisotropy of laser emission in monoclinic Nd:ScYSiO5 crystals cut along the optical indicatrix axes
In this Letter, we demonstrate the anisotropy of laser emission in disordered Nd : ScYSiO 5 Y X X Z
140.3380 Laser materials 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched Fabrication of grating structures on silicon carbide by femtosecond laser irradiation and wet etching Download:1367次
Download:1367次
 Download:1367次
Download:1367次A method for fabricating deep grating structures on a silicon carbide (SiC) surface by a femtosecond laser and chemical-selective etching is developed. Periodic lines corresponding to laser-induced structure change (LISC) are formed by femtosecond laser irradiation, and then the SiC material in the LISC zone is removed by a mixed solution of hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid to form grating grooves. Grating grooves with a high-aspect ratio of approximately 25 are obtained. To obtain a small grating period, femtosecond laser exposure through a phase mask was used to fabricate grating structures with a 1.07 μm period on the surface of the SiC.
140.7090 Ultrafast lasers 230.4000 Microstructure fabrication 160.6000 Semiconductor materials The use of red light or near-infrared radiation as a luminescent probe for in vivo bio imaging is crucial in order to restrict the strong absorption of short-wavelength light below 600 nm in tissue. It is demonstrated that the emission color of Yb/Ho codoped NaYF 4 Ce 3 + NaYF 4 : Yb / Ho Ce 3 + NaYF 4 : Yb / Ho Ce 3 + NaYF 4 : Yb 3 + 50 % NaYF 4 : Ho 3 + 0.5 % NaYF 4 : Yb / Ho / Ce Ce 3 + 160.2540 Fluorescent and luminescent materials 160.4760 Optical properties
A highly transparent Eu 3 + CaGdAlO 4 f – f Eu 3 + D 0 5 – F 7 2 D 0 5 – F 7 1 Eu 3 + Eu : D 0 5
160.2540 Fluorescent and luminescent materials 300.6170 Spectra 260.1180 Crystal optics 160.4670 Optical materials Efficiency balance of a light guide plate with microstructures for a see-through head-mounted display Download:969次
Download:969次
 Download:969次
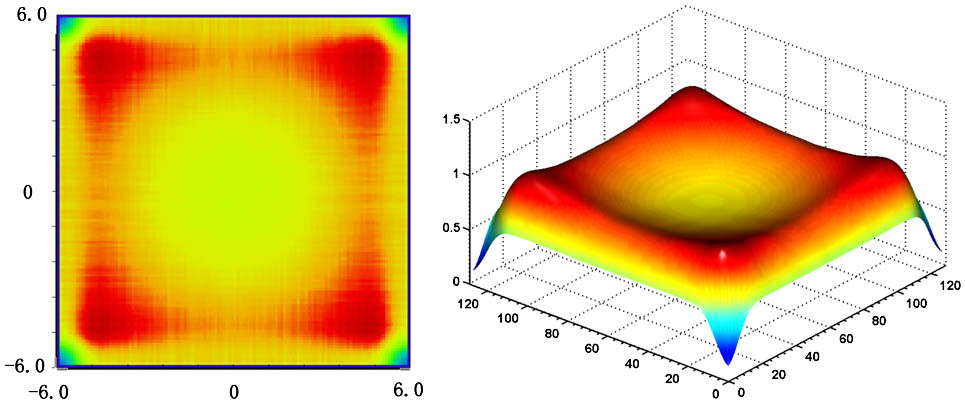
Download:969次The efficiency balance phenomenon for see-through head-mounted displays with different microstructure conditions can be found both theoretically and using optical simulation software. A simple mathematical calculation is used to determine the relationship between the real image (see-through function) energy and the virtual image energy. The simulation is based on factors taken from previous research studies. It is found that the balance value of the optical efficiency remains almost constant (66.63% to 67.38%) under different microstructure conditions. In addition, suitable conditions for the microstructures in see-through head-mounted displays for daily applications can be predicted.
220.4830 Systems design 120.2820 Heads-up displays 220.2740 Geometric optical design In this study, a new method utilizing surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensing technology based on the phase and angular interrogations for measuring the refractive index of a liquid prism is presented. An orthogonal sample box that combined the functions of a prism, cell box, and mirror is adopted to simplify the system and provide the convenience to implement the phase and angular interrogations. The angular interrogation is achieved by the motorized rotation stage with the new sample box, and the phase interrogation is achieved by the linear polarization interferometry between the s - and p -polarization components. The amplitude reflectivity and the phase angle, which are the functions of the incident angle, are obtained by the reflection intensity and the interference intensity of the lights directly. A sensitivity of 7.5 × 10 7
240.6680 Surface plasmons 280.4788 Optical sensing and sensors Short-wave infrared detector with double barrier structure and low dark current density Download:897次
Download:897次
 Download:897次
Download:897次Short-wave infrared (SWIR) detectors combining AlAs / In 0.53 Ga 0.47 As / AlAs In 0.53 Ga 0.47 As 3.77 × 10 14 W / Hz 1 / 2
250.0040 Detectors 230.5160 Photodetectors 160.1890 Detector materials 060.5565 Quantum communications We report on our high-contrast laser based on high-contrast, high-energy seed injection, low-gain optical parametric chirped pulse amplification (OPCPA), and Nd:glass amplifiers, which can be used as the high-contrast front end of a high-power Nd:glass chirped pulse amplification (CPA) laser system. The energy of the stretched 1053 nm high-contrast seed pulse increases to 60 μJ by optimizing the frequency doubling crystal in the pulse cleaning device. After passing through a two-stage low-gain OPCPA, a 2-pass 2-rod Nd:glass amplifier, and a compressor the amplified pulse of 131 mJ / 282 fs 10 7 – 10 8
320.7090 Ultrafast lasers 190.4410 Nonlinear optics, parametric processes 140.3280 Laser amplifiers 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦