中国科学院 长春光学精密机械与物理研究所,吉林 长春 130033
液晶空间光调制器通过改变驱动电压强度控制液晶分子排布实现对光的调制。紫外区域可用的液晶空间光调制器随光聚合式3D打印等应用的兴起,重要性日益显现。然而绝大多数液晶材料都是有机物,在紫外波段存在光吸收和光反应。为了拓宽液晶材料的应用波段,本文通过选择在应用波段不发生紫外吸收和光反应的官能团,设计了一类可在325~400 nm波段应用不发生光吸收和光反应的液晶材料,并对液晶材料的紫外-可见光光谱进行仿真以验证设计的合理性。将耐紫外液晶化合物配置成混合液晶材料后与常见的两种混合液晶材料的紫外稳定性进行比较。在经过120 min的325 nm紫外光源的辐照后,液晶材料的吸光度和相变温度几乎不变,双折射率变化0.04%,阈值电压变化1.39%,响应时间变化0.32%。
液晶材料 紫外稳定性 双折射率 liquid crystal material UV stability birefringence
液晶材料是信息显示设备中的重要组成部分, 其在外场作用下所表现的高双折射特性是其被用于显示的关键条件。利用强太赫兹波作为外场, 激发液晶5CB材料的双折射效应。结合太赫兹时域光谱系统通过测量不同偏振的太赫兹波的透过率, 研究了太赫兹场致液晶在太赫兹波段的双折射效应。分析了液晶的双折射效应与外场强的变化关系、频率响应特性等方面。研究结果表明在强场太赫兹波激发下, 液晶的双折射现象随场强的增大而增大, 双折射值与外部场强平方成正比, 且液晶5CB对于太赫兹激发的双折射效应存在一定的阈值。
物理光学 液晶 双折射 太赫兹强场 偏振 阈值 physical?optics liquid crystal birefringence terahertz strong field polarization threshold
1 南通大学 机械工程学院, 南通 226019
2 清华大学 精密仪器系 精密测试技术及仪器国家重点实验室, 北京 100084
为了研究基于激光回馈的偏振跳变效应与相位延迟间的内在联系, 采用微片Nd∶YAG激光器(中心波长1064 nm)为光源, 回馈腔内置两个相对旋转的λ/4波片改变相位延迟, 在调谐回馈腔长的过程中研究了激光器的光强输出和偏振态变化。结果表明, 随着回馈腔内相位延迟增大, 偏振跳变点的凹陷逐渐加深, 两个偏振态的光强调制波形宽度趋于相同; 当回馈腔中相位延迟为90°时, 两正交偏振态在一个强度调制周期内持续时间相同, 每一次偏振跳变对应回馈腔长改变λ/4。此不同相位延迟下偏振跳变点的变化规律, 为1064 nm波长下的波片相位延迟测量提供了潜在方法, 同时相位延迟对激光器输出光强曲线的整形、为激光回馈条纹(自混合干涉条纹)的光学细分提供了依据。
激光光学 偏振跳变 微片激光器 外腔双折射回馈 laser optical polarization flipping microchip laser external-cavity birefringence feedback
1 中国航天科技集团有限公司量子工程研究中心, 北京 100194
2 北京航天控制仪器研究所, 北京 100039
原子气室作为量子仪表的核心部件, 其稳定性和寿命是决定量子仪表长期可靠工作的主要因素。在制备原子气室过程中, 玻璃高温熔接产生的残余应力会影响气室的力学特性及光学性能, 应力过大将导致气室在加工过程中发生炸裂, 并在后期应力释放过程中出现裂纹, 造成气室失效。测量和消除原子气室玻壳残余应力对提高原子气室的寿命和可靠性有重要意义。利用双折射应力测量仪对原子气室玻壳应力分布进行无损测量, 测量结果具有良好的一致性和重复性。经过退火处理后, 5支玻壳的应力最大值、平均值和标准差的平均值降幅分别达到81.35%、75.67%和77.32%, 表明消除应力取得了良好的效果。
原子气室 高硼硅玻壳 残余应力 退火处理 双折射原理 vapor cell high borosilicate glass shell residual stress annealing treatment birefringence principle
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Fuzhou 350002, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Fujian Science and Technology Innovation Laboratory for Optoelectronic Information of China, Fuzhou 350108, China
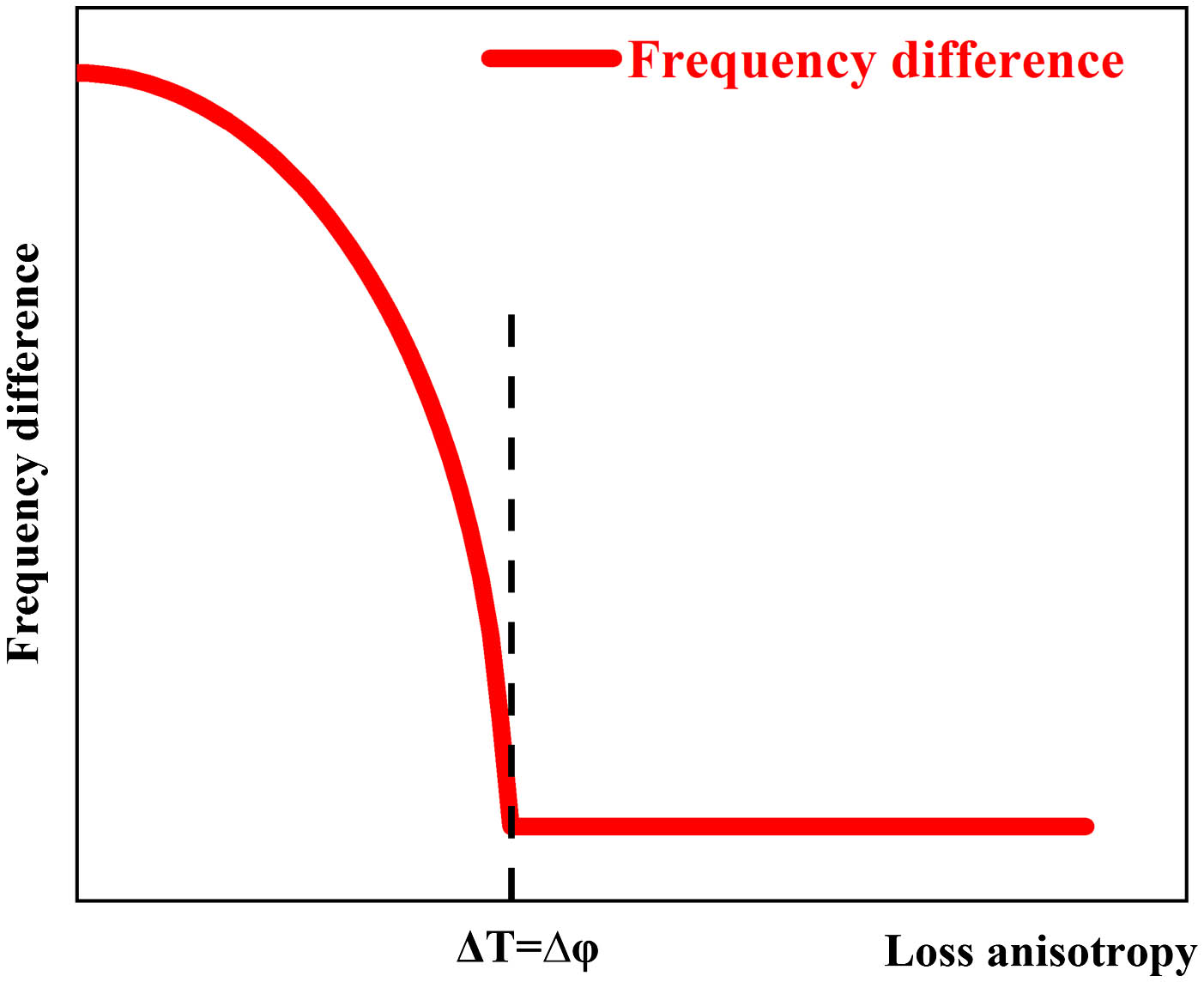
In this paper, the frequency difference of the eigen polarization modes of the Nd:YAG crystal laser at different polarization ratios is experimentally studied, and to the best of our knowledge, the correlation between the frequency difference of the eigenmodes and the output polarization degree is reported for the first time. Combined with the analysis of the polarization beam profile, it is proved that the polarized laser produced by the isotropic crystal is due to the frequency locking of the eigen polarization modes. The weak birefringence in the crystal causes the round-trip phase difference of the orthogonal polarization modes, which leads to the frequency difference between the polarization modes. By the adjustment of the cavity mirror, the anisotropic loss will interact with the round-trip phase difference. The eigen polarization modes can reach frequency degeneration, and then be coherently combined to produce linearly polarized laser output. This work provides a useful reference for understanding the physical mechanism of polarized lasers realized by isotropic crystals.
linear polarization frequency difference weak birefringence Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(11): 111401
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Specialty Fiber Optics and Optical Access Networks, Joint International Research Laboratory of Specialty Fiber Optics and Advanced Communication, School of Communication and Information Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
Fiber quarter-wave plates and magneto-optical fibers are important components that greatly affect the sensitivity of fiber-optic current sensors. A Tb:YAG crystal-derived silica fiber (TYDSF) was fabricated using a laser-heating drawing technique. The linear birefringence of TYDSF was measured as by a microscope birefringence measurement instrument. A fiber quarter-wave plate was fabricated by TYDSF at 1310 nm, which produced circularly polarized light with a polarization extinction ratio of 0.34 dB. Additionally, the linear birefringence of TYDSF was decreased by 22% by annealing at 750°C for 7 h, and the Verdet constants of annealed TYDSF were measured to be 9.83, 6.67, and at 808, 980, and 1310 nm, respectively.
Faraday effect linear birefringence fiber quarter-wave plate Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(11): 110601

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai, China
2 Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden – Rossendorf, Dresden, Germany
3 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China
4 Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany
Polarimetry is a highly sensitive method to quantify changes of the polarization state of light when passing through matter and is therefore widely applied in material science. The progress of synchrotron and X-ray free electron laser (XFEL) sources has led to significant developments of X-ray polarizers, opening perspectives for new applications of polarimetry to study source and beamline parameters as well as sample characteristics. X-ray polarimetry has shown to date a polarization purity of less than $1.4\times {10}^{-11}$ , enabling the detection of very small signals from ultrafast phenomena. A prominent application is the detection of vacuum birefringence. Vacuum birefringence is predicted in quantum electrodynamics and is expected to be probed by combining an XFEL with a petawatt-class optical laser. We review how source and optical elements affect X-ray polarimeters in general and which qualities are required for the detection of vacuum birefringence.
birefringence polarimetry polarizer quantum electrodynamics X-rays High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2023, 11(6): 06000e71
1 海南师范大学物理与电子工程学院海南省激光技术与光电功能材料重点实验室,海南 海口 571158
2 齐鲁工业大学(山东省科学院)海洋仪器仪表研究所,山东 青岛 266061
3 青岛海洋科技中心,山东 青岛 266237
为了进一步提高传统保偏光纤的双折射,设计了一种高双折射椭圆芯类矩形保偏光纤,该光纤具有一个椭圆芯和两个对称的类矩形应力区。采用数值模拟的方法,全面研究了类矩形应力区的尺寸和纤芯的椭圆度对保偏光纤双折射特性的影响。通过优化参数得到椭圆芯类矩形保偏光纤在1550 nm波长下的双折射为8.0794×10-4,与传统熊猫型保偏光纤的双折射相比增加了近一倍。此外,还研究了所设计光纤在C通信波段(1530~1565 nm)内双折射与波长变化的关系。该光纤结构简单,具有应用于光纤通信和光纤传感领域的潜力。
保偏光纤 保偏性能 模式双折射 结构优化 光学学报
2023, 43(20): 2006007
1 浙江大学 光电科学与工程学院,浙江杭州3004
2 宁波永新光学股份有限公司,浙江宁波315040
3 中北大学 山西省光电信息与仪器工程技术研究中心,山西太原00051
为了实现对光学材料、光学元件的快速、高精度应力双折射测试评估分析,本文提出了一种基于双弹光级联差频调制的应力双折射二维分布测量方案。将两个工作在不同频率的弹光调制器级联,构成偏振测量装置。光学材料和元件的应力双折射延迟量和快轴方位角参数,被加载到偏振测量装置的调制信号中;采用数字锁相技术,提取调制信号的基频项和差频项,然后完成应力双折射延迟量和快轴方位角两个参数求解;按照原理分析,研制了测试系统,并完成了系统初始偏移值定标;采用波片进行了测量精度和重复性测试,并完成了BK7玻璃样品的应力双折射分布测量实验。实验结果表明,该系统的快轴测量重复性为0.01°,双折射延迟量测量重复性为0.02 nm,单数据点测量时间小于200 ms。本文方案实现了高速、高精度和高重复度的应力双折射测量,同时具备应力双折射二维分布测量能力,可为波片、玻璃或晶体等光学材料双折射测量分析和评估提供有效手段。
弹光调制 差频调制 应力双折射 延迟量 快轴方位角 photoelastic modulation difference frequency modulation stress birefringence retardance fast axis azimuth 光学 精密工程
2023, 31(18): 2647
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 iXblue Photonics, Rue Paul Sabatier, 22300 Lannion, France
2 iXblue, 34 Rue de la Croix de Fer, 78100 Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
3 Laboratoire Hubert Curien, UJM-CNRS-IOGS, 18 Rue Professeur Benoît Lauras, 42000 Saint-Etienne, France
A recent JEOS-RP publication proposed Comments about Dispersion of Light Waves, and we present here complementary comments for birefringence dispersion in polarization-maintaining (PM) fibers, and for its measurement techniques based on channeled spectrum analysis. We start by a study of early seminal papers, and we propose additional explanations to get a simpler understanding of the subject. A geometrical construction is described to relate phase birefringence to group birefringence, and it is applied to the measurement of several kinds of PM fibers using stress-induced photo-elasticity, or shape birefringence. These measurements confirm clearly that the difference between group birefringence and phase birefringence is limited to 15–20% in stress-induced PM fibers (bow-tie, panda, or tiger-eye), but that it can get up to a 3-fold factor with an elliptical-core (E-core) fiber. There are also surprising results with solid-core micro-structured PM fibers, that are based on shape birefringence, as E-core fibers.
Birefringence Birefringence dispersion Channeled-spectrum analysis Group birefringence Phase birefringence Polarization-maintaining fiber Polarization-mode dispersion Journal of the European Optical Society-Rapid Publications
2023, 19(1): 2022014





