2024, 22(1) Column
Diffraction, Gratings, and Holography Fiber Optics and Optical Communications Imaging Systems and Image Processing Instrumentation, Measurement, and Optical Sensing Integrated Optics Lasers, Optical Amplifiers, and Laser Optics Optical Materials Biophotonics Nonlinear Optics Optoelectronics Spectroscopy Ultrafast Optics and Attosecond/High-field Physics Infrared and Terahertz Photonics Microwave Photonics
Chinese Optics Letters 第22卷 第1期
Aiming for suppressing side-mode and spectrum broadening, a slit beam-shaping method and super-Gaussian apodization processing for femtosecond laser point-by-point (PbP) inscription technology of fiber Bragg gratings (FBGs) are reported here. High-quality FBGs, featuring narrow bandwidth of less than 0.3 nm, high reflectivity above 85%, low insertion loss (0.21 dB), and low cladding loss (0.82 dB), were obtained successfully. By a semi-automatic PbP inscription process, an array consisting of six FBGs, exhibiting almost no side-mode peaks with high suppression ability and narrow bandwidth, was fabricated along three independently developed single-mode fibers with an interval of 20 mm.
femtosecond laser processing fiber Bragg grating slit beam shaping We experimentally transmit eight wavelength-division-multiplexing (WDM) channels, 16 quadratic-amplitude-modulation (QAM) signals at 32-GBaud, over 1000 km few mode fiber (FMF). In this experiment, we use WDM, mode division multiplexing, and polarization multiplexing for signal transmission. Through the multiple-input–multiple-output (MIMO) equalization algorithms, we achieve the total line transmission rate of 4.096 Tbit/s. The results prove that the bit error rates (BERs) for the 16QAM signals after 1000 km FMF transmission are below the soft-decision forward-error-correction (SD-FEC) threshold of
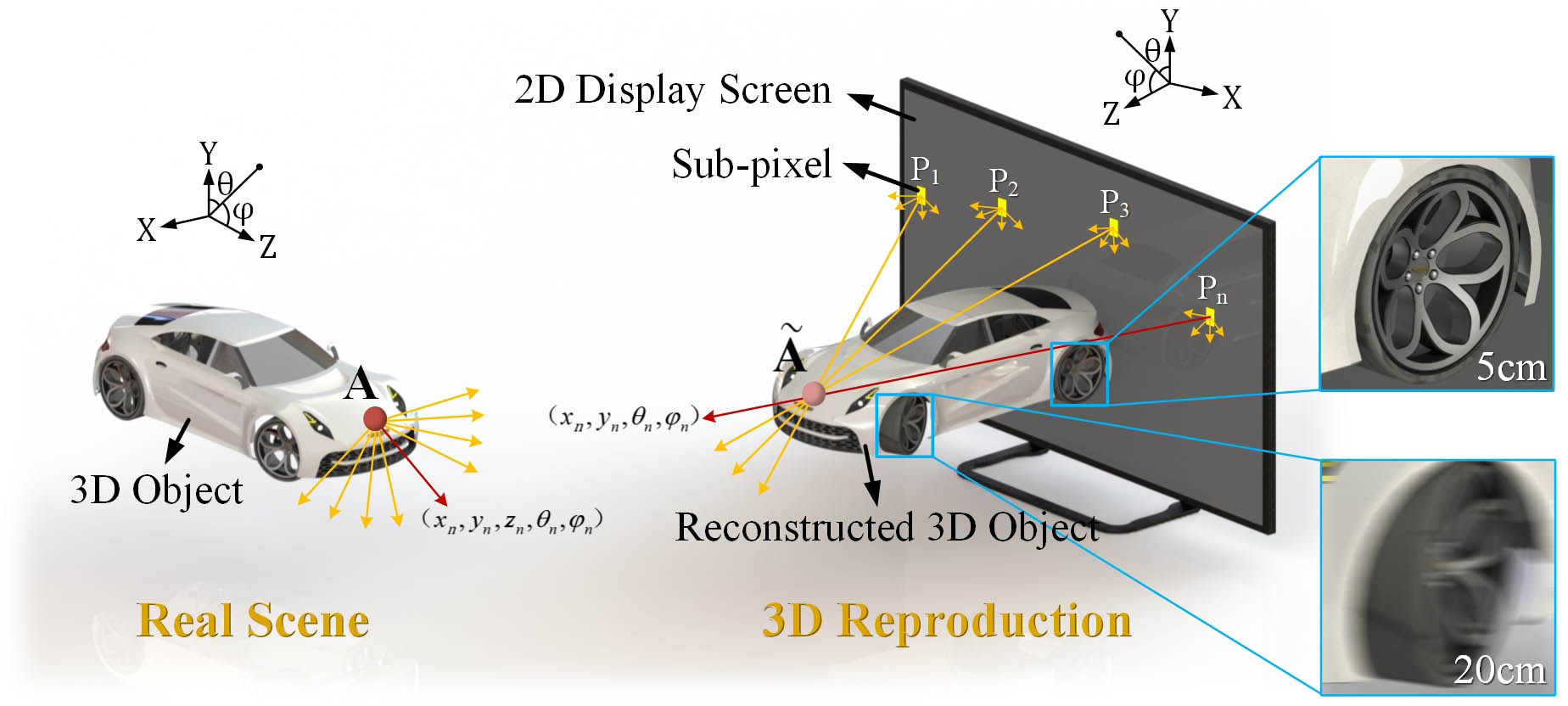
optical fiber communication mode division multiplexing few-mode fiber multiple-input–multiple-output high-capacity transmission long-distance transmission A concept of divergence angle of light beams (DALB) is proposed to analyze the depth of field (DOF) of a 3D light-field display system. The mathematical model between DOF and DALB is established, and the conclusion that DOF and DALB are inversely proportional is drawn. To reduce DALB and generate clear depth perception, a triple composite aspheric lens structure with a viewing angle of 100° is designed and experimentally demonstrated. The DALB-constrained 3D light-field display system significantly improves the clarity of 3D images and also performs well in imaging at a 3D scene with a DOF over 30 cm.
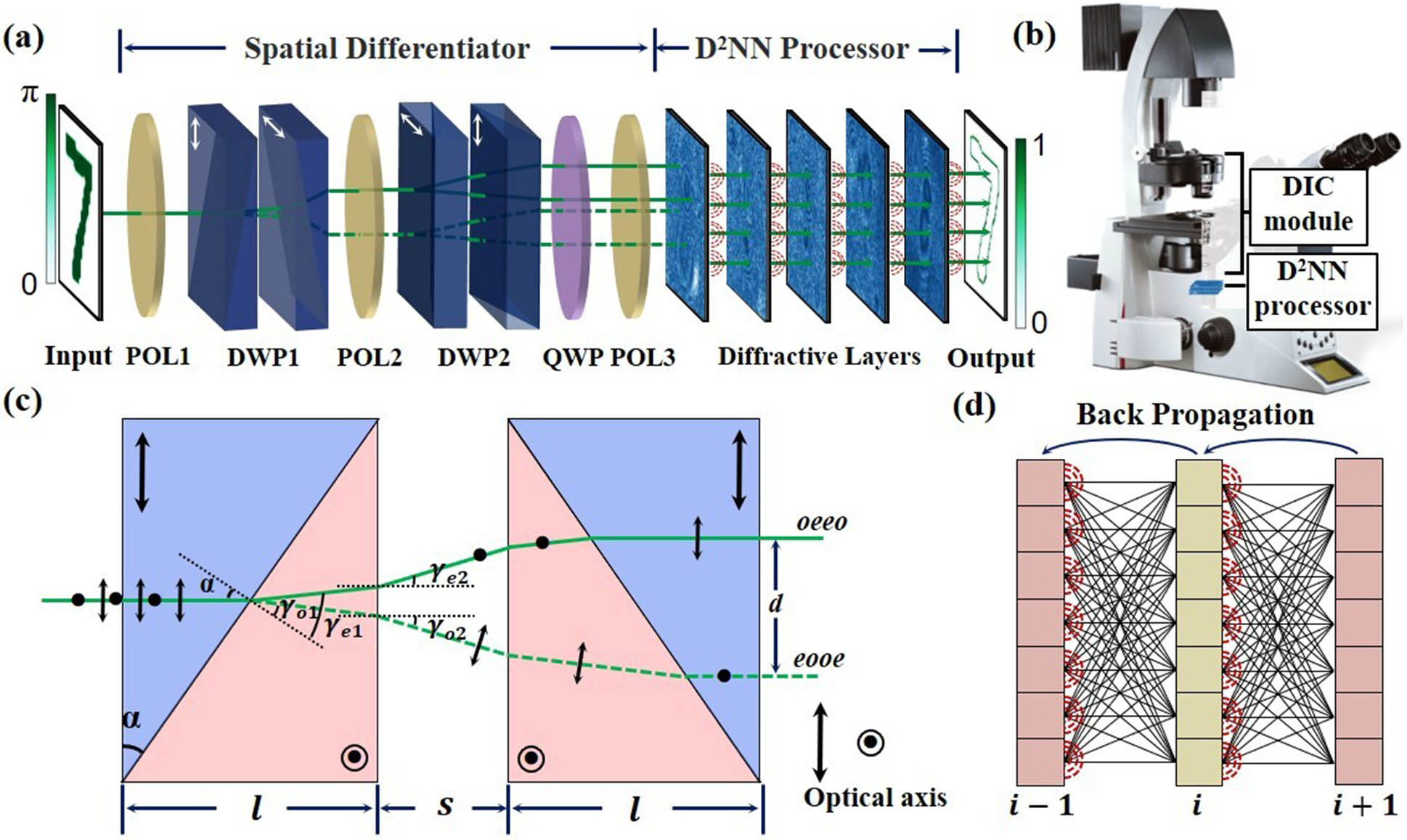
3D light-field display depth of field divergence angle of light beams compound lens Edge detection for low-contrast phase objects cannot be performed directly by the spatial difference of intensity distribution. In this work, an all-optical diffractive neural network (DPENet) based on the differential interference contrast principle to detect the edges of phase objects in an all-optical manner is proposed. Edge information is encoded into an interference light field by dual Wollaston prisms without lenses and light-speed processed by the diffractive neural network to obtain the scale-adjustable edges. Simulation results show that DPENet achieves F-scores of 0.9308 (MNIST) and 0.9352 (NIST) and enables real-time edge detection of biological cells, achieving an F-score of 0.7462.
diffractive neural network edge detection phase objects We demonstrate a simultaneous transmission of time-frequency and data over a 160-km urban business network in Shanghai. The signals are transmitted through a cascaded optical link consisting of 48 km and 32 km, which are connected by an optical relay. The metrological signals are inserted into the communication network using dense wavelength division multiplexing. The influence of the interference between different signals has been discussed. The experimental results demonstrate that the radio frequency (RF) instability can reach
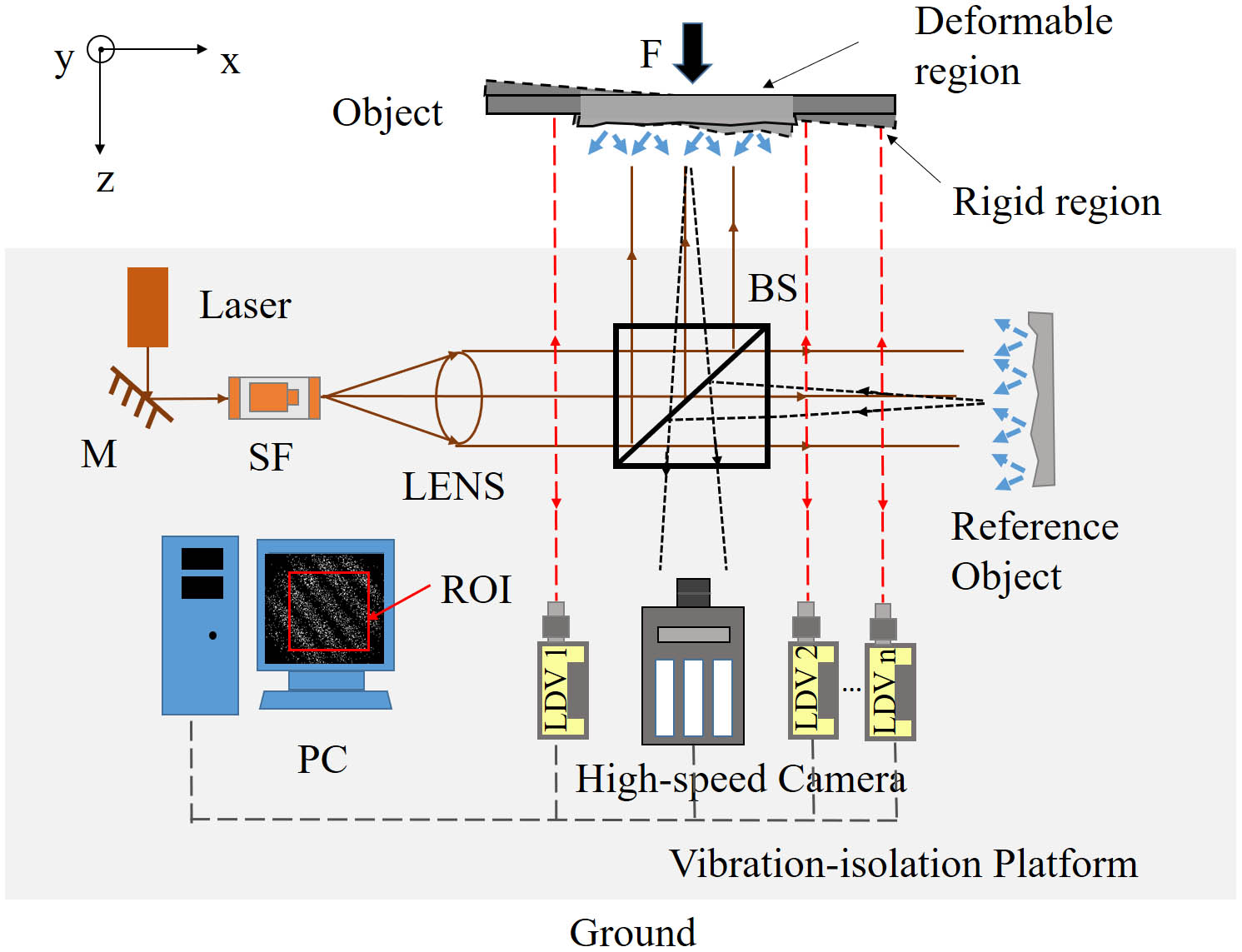
simultaneous transmission radio frequency transfer communication network wavelength multiplexing A new electronic speckle pattern interferometry method is proposed to realize in situ deformation measurements. The feature of the method is the combination of a high-speed camera and multiple laser Doppler vibrometers (LDVs) for synchronous measurements. The high-speed camera is used to record and select effective interferograms, while the LDVs are used to measure the rigid body displacement caused by vibrations. A series of effective interferograms with known shifted phase values are obtained to calculate the deformation phase. The experimental results show that the method performs well in measuring static and dynamic deformations with high accuracy in vibrating environments.
speckle pattern interferometry laser Doppler vibrometers Optical coherence tomography (OCT) allows a direct and precise measurement of laser welding depth by coaxially measuring the keyhole depth and can be used for process monitoring and control. When OCT measurement was taken during single-beam laser welding, the keyhole instability of aluminum welding resulted in highly scattered OCT data and complicated the welding depth extraction methods. As a combination of an inner core beam and an outer ring beam, a novel adjustable ring mode (ARM) laser for producing a stable keyhole was applied to the OCT measurement. Different ARM laser power arrangements were conducted on aluminum and copper. The results indicated that the ring beam greatly improved the stability of the core beam-induced keyhole, and smooth welding depth can be extracted from the concentrated OCT data.
optical coherence tomography adjustable ring mode laser laser welding welding depth We propose an absolute distance measurement method that employs heterodyne and superheterodyne combined interferometers to achieve synchronous detection and demodulation of multiwavelengths. Coarse and fine synthetic wavelengths are generated by a dual-longitudinal-mode He–Ne laser and four acoustic optical frequency shifters. Further, to improve phase synchronization measurement for multiwavelengths, we analyze the demodulation characteristics of coarse and fine measurement signals and adopt a demodulation method suitable for both signals. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can achieve high-precision synchronous demodulation of multiwavelengths, and standard deviation is 1.7 × 10-5 m in a range of 2 m.
multiwavelength absolute distance superheterodyne interferometry phase synchronization A flexible-grid
integrated optics optical waveguide mode- and wavelength-selective switch Mode splitters that directly separate modes without changing their orders are highly promising to improve the flexibility of the mode-division multiplexing systems. In this paper, we design a high-performance mode splitter on the silicon-on-insulator platform with a compact footprint of 14 µm× 2.5 µm using an inverse design method based on shape optimization. The fabrication of this mode splitter requires only a single lithography step and exhibits good fabrication tolerances. The experimental results show that the proposed device exhibits state-of-the-art insertion loss (<0.9 dB) and cross talk (<-16 dB) over a broad bandwidth (1500–1600 nm). Furthermore, the shape optimization method used is implemented to design a dual-mode (de)multiplexer, and the experimental results fulfill the design objective, demonstrating the excellent generality of the design method in this paper.
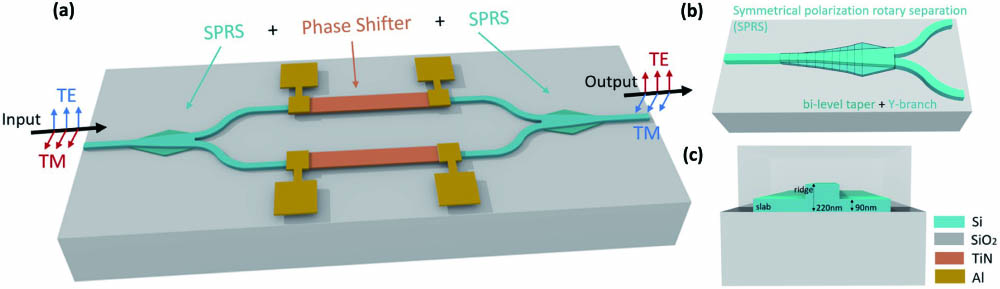
integrated optics inverse design mode splitter Silicon waveguides typically exhibit optical anisotropy, which leads to polarization correlation and single-polarization operations. This consequently creates a demand for polarization-control devices. This paper introduces a CMOS-compatible O-band reconfigurable TE/TM polarization rotator comprising two symmetrical polarization rotator–splitters and phase shifters. This configuration enables dynamic conversion of any linear polarization to its quadratic equivalent. Experimental results indicate that the reconfigurable polarization rotator exhibits an insertion loss of less than 1.5 dB. Furthermore, the bandwidth for a polarization extinction ratio beyond 15 dB exceeds 60 nm.
silicon-based optoelectronics polarization rotation polarization switch The dual-mode stabilization scheme has been demonstrated as an efficient way to stabilize laser frequency. In this study, we propose a novel dual-mode stabilization scheme that employs a sizable Fabry–Pérot cavity instead of the microcavity used in previous studies and has enabled higher bandwidth for locking. The results demonstrate a 30-fold reduction in laser frequency drift, with frequency instability below 169 kHz for integration time exceeding 1 h and a minimum value of 33.8 kHz at 54 min. Further improvement could be achieved by optimizing the phase locking. This scheme has potential for use in precision spectroscopic measurement.
We present a study on a watt-level acousto-optically Q-switched Pr:YLF laser at three different repetition rates (10 kHz, 20 kHz, and 50 kHz) for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. The corresponding average output powers and pulse widths were measured to be 1.14 W, 1.2 W, and 1.32 W, and 40 ns, 52 ns, and 80 ns, respectively. A maximum pulse energy of 0.11 mJ was obtained, corresponding to a peak power of up to 2.8 kW at a repetition rate of 10 kHz. The simulated dynamics of a fast Q-switched Pr:YLF laser is in agreement with the experiment. The laser’s ability to generate stable pulses with high peak power and short pulse width makes it highly desirable for various practical applications, such as laser machining and material processing.
red pulsed laser Pr:YLF diode pump acousto-optical We present our efforts towards power scaling of Er:Lu2O3 lasers at 2.85 µm. By applying a dual-end diode-pumped resonator scheme, we achieve an output power of 14.1 W at an absorbed pump power of 59.7 W with a slope efficiency of 26%. In a single-end pumped resonator scheme, an output power of 10.1 W is reached under 41.9 W of absorbed pump power. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first single crystalline mid-infrared rare-earth-based solid-state laser with an output power exceeding 10 W at room temperature.
high-power continuous-wave laser mid-infrared laser dual-end pump scheme Toroidal multipole is a special current distribution that has many different characteristics from electric multipole and magnetic multipole distributions. Because of its special properties, the toroidal dipole is a research hotspot in the field of metamaterials and nanophotonics. However, the low scattering of the toroidal dipole moment makes its excitation a challenging task. At present, there are relatively few studies on its specific engineering applications. In this paper, by slotting in the rectangular cavity, the excitation of an equivalent toroidal dipole is successfully achieved over a wide frequency range of 53–58 GHz. Results indicate that under the action of the toroidal dipole, the
toroidal dipole vector beams vector vortex beams We propose a laser speckle contrast imaging method based on uniting spatiotemporal Fourier transform. First, the raw speckle images are entirely transformed to the spatiotemporal frequency domain with a three-dimensional (3D) fast Fourier transform. Second, the dynamic and static speckle components are extracted by applying 3D low-pass and high-pass filtering in the spatiotemporal frequency domain and inverse 3D Fourier transform. Third, we calculate the time-averaged modulation depth with the average of both components to map the two-dimensional blood flow distribution. The experiments demonstrate that the proposed method could effectively improve computational efficiency and imaging quality.
uniting spatiotemporal Fourier transform laser speckle contrast image fluctuation modulation 3D Fourier transform We propose a spatially chirped quasi-phase-matching (QPM) scheme that enables ultrabroadband second-harmonic-generation (SHG) by using a fan-out QPM grating to frequency-convert a spatially chirped fundamental wave. A “zero-dispersion” 4f system maps the spectral contents of ultrabroadband fundamental onto different spatial coordinates in the Fourier plane, where the fundamental is quasi-monochromatic locally in picosecond duration, fundamentally canceling high-order phase mismatch. A fan-out QPM grating characterized by a linear variation of the poling period along the transverse direction exactly supports the QPM of the spatially chirped beam. We theoretically demonstrate the SHG of an 810-nm, 12.1-fs pulse into a 405-nm, 10.2-fs pulse with a conversion efficiency of 77%.
nonlinear optics second-harmonic generation few-cycle pulse Radio frequency/microwave-directed energy sources using wide bandgap SiC photoconductive semiconductors have attracted much attention due to their unique advantages of high-power output and multi-parameter adjustable ability. Over the past several years, benefitting from the sustainable innovations in laser technology and the significant progress in materials technology, megawatt-class output power electrical pulses with a flexible frequency in the P and L microwave wavebands have been achieved by photoconductive semiconductor devices. Here, we mainly summarize and review the recent progress of the high-power photonic microwave generation based on the SiC photoconductive semiconductor devices in the linear modulation mode, including the mechanism, system architecture, critical technology, and experimental demonstration of the proposed high-power photonic microwave sources. The outlooks and challenges for the future of multi-channel power synthesis development of higher power photonic microwave using wide bandgap photoconductors are also discussed.
high-power photonic microwave wide bandgap photoconductive semiconductor devices linear modulation multi-parameter adjustable microwave generation multi-channel power synthesis In this paper, we demonstrate nBn InAs/InAsSb type II superlattice (T2SL) photodetectors with AlAsSb as the barrier that targets mid-wavelength infrared (MWIR) detection. To improve operating temperature and suppress dark current, a specific Sb soaking technique was employed to improve the interface abruptness of the superlattice with device passivation using a
mid-wavelength infrared photodetector InAs/InAsSb superlattice high operating temperature dark current The dynamics of water within a nanopool of a reverse micelle is heavily affected by the amphiphilic interface. In this work, the terahertz (THz) spectra of cyclohexane/Igepal/water nonionic reverse micelle mixture are measured by THz time-domain spectroscopy and analyzed with two Debye models and complex permittivity of background with volume ratios. Based on the fitted parameters of bulk and fast water, the molar concentration of all kinds of water molecules and hydration water molecule number per Igepal molecule are calculated. We find that slow hydration water has the highest proportion in water when the radius parameter
reverse micelle water dynamics THz spectroscopy The characteristics of plasmas play an important role in femtosecond laser filament-based applications. Spectroscopic analysis is used to experimentally investigate the plasma density and its temperature of the air filament under different pulse repetition rates. In our experiments, the measured average plasma density of the filament is
femtosecond laser filamentation cumulative effects electron density Two-dimensional (2D) van der Waals materials have attracted tremendous attention due to their versatile physical properties and flexible manipulation approaches. Among the various types of van der Waals materials,
van der Waals terahertz carrier dynamics Metalenses are essential components in terahertz imaging systems. However, without careful design, they show limited field of view and their practical applications are hindered. Here, a wide-angle metalens is proposed whose structure is optimized for focusing within the incident angles of
terahertz metalens wide-angle Gaussian formula High accuracy and time resolution optical transfer delay (OTD) measurement is highly desired in many multi-path applications, such as optical true-time-delay-based array systems and distributed optical sensors. However, the time resolution is usually limited by the frequency range of the probe signal in frequency-multiplexed OTD measurement techniques. Here, we proposed a time-resolution enhanced OTD measurement method based on incoherent optical frequency domain reflectometry (I-OFDR), where an adaptive filter is designed to suppress the spectral leakage from other paths to break the resolution limitation. A weighted least square (WLS) cost function is first established, and then an iteration approach is used to minimize the cost function. Finally, the appropriate filter parameter is obtained according to the convergence results. In a proof-of-concept experiment, the time-domain response of two optical links with a length difference of 900 ps is successfully estimated by applying a probe signal with a bandwidth of 400 MHz. The time resolution is improved by 2.78 times compared to the theoretical resolution limit of the inverse discrete Fourier transform (iDFT) algorithm. In addition, the OTD measurement error is below
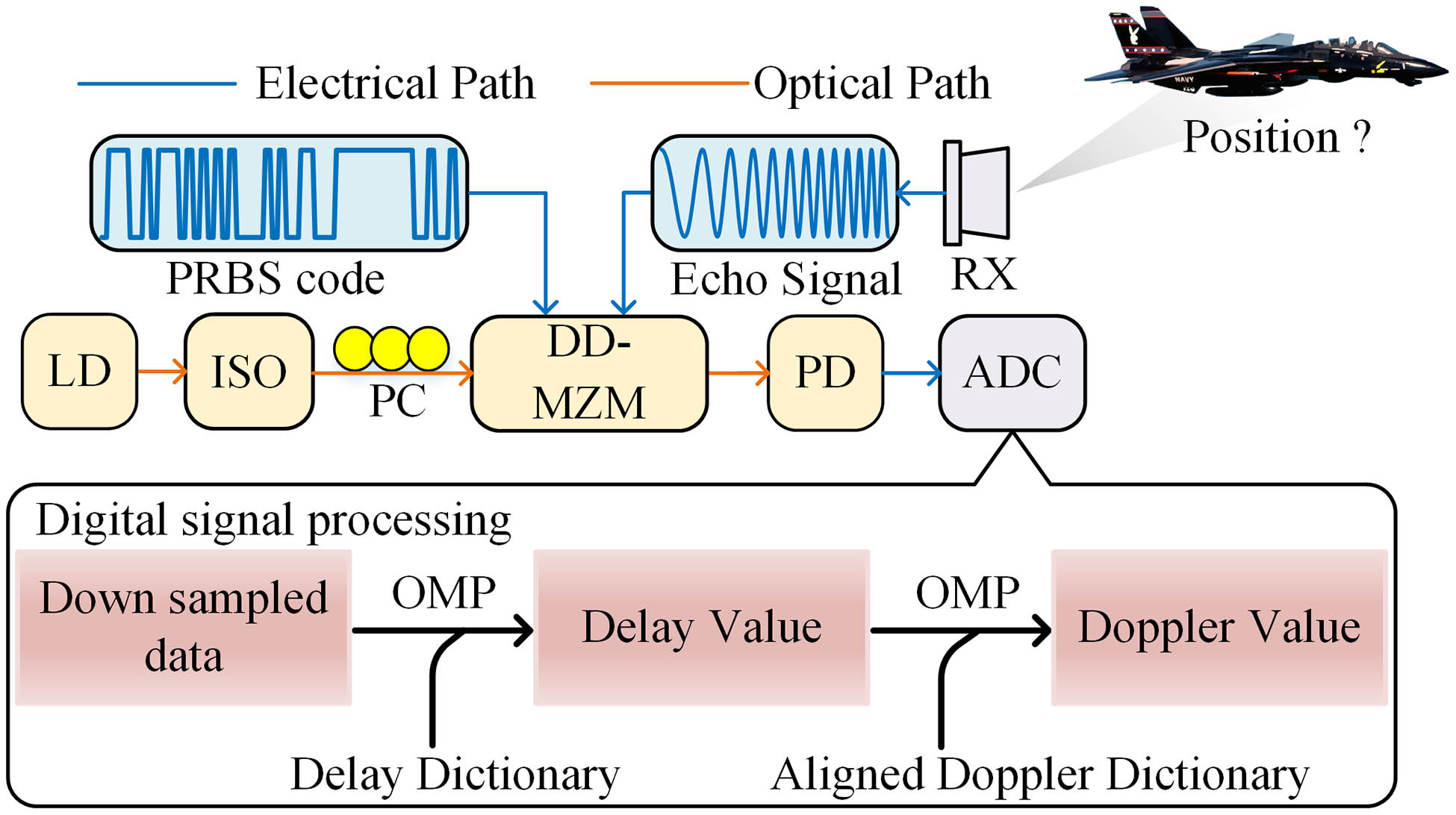
optical transfer delay measurement time resolution enhancement incoherent OFDR adaptive filtering A sub-Nyquist radar receiver based on photonics-assisted compressed sensing is proposed. Cascaded dictionaries are applied to extract the delay and the Doppler frequency of the echo signals, which do not need to accumulate multiple echo periods and can achieve better Doppler accuracy. An experiment is performed. Radar echoes with different delays and Doppler frequencies are undersampled and successfully reconstructed to obtain the delay and Doppler information of the targets. Experimental results show that the average reconstruction error of the Doppler frequency is 5.33 kHz using an 8-μs radar signal under the compression ratio of 5. The proposed method provides a promising solution for the sub-Nyquist radar receiver.
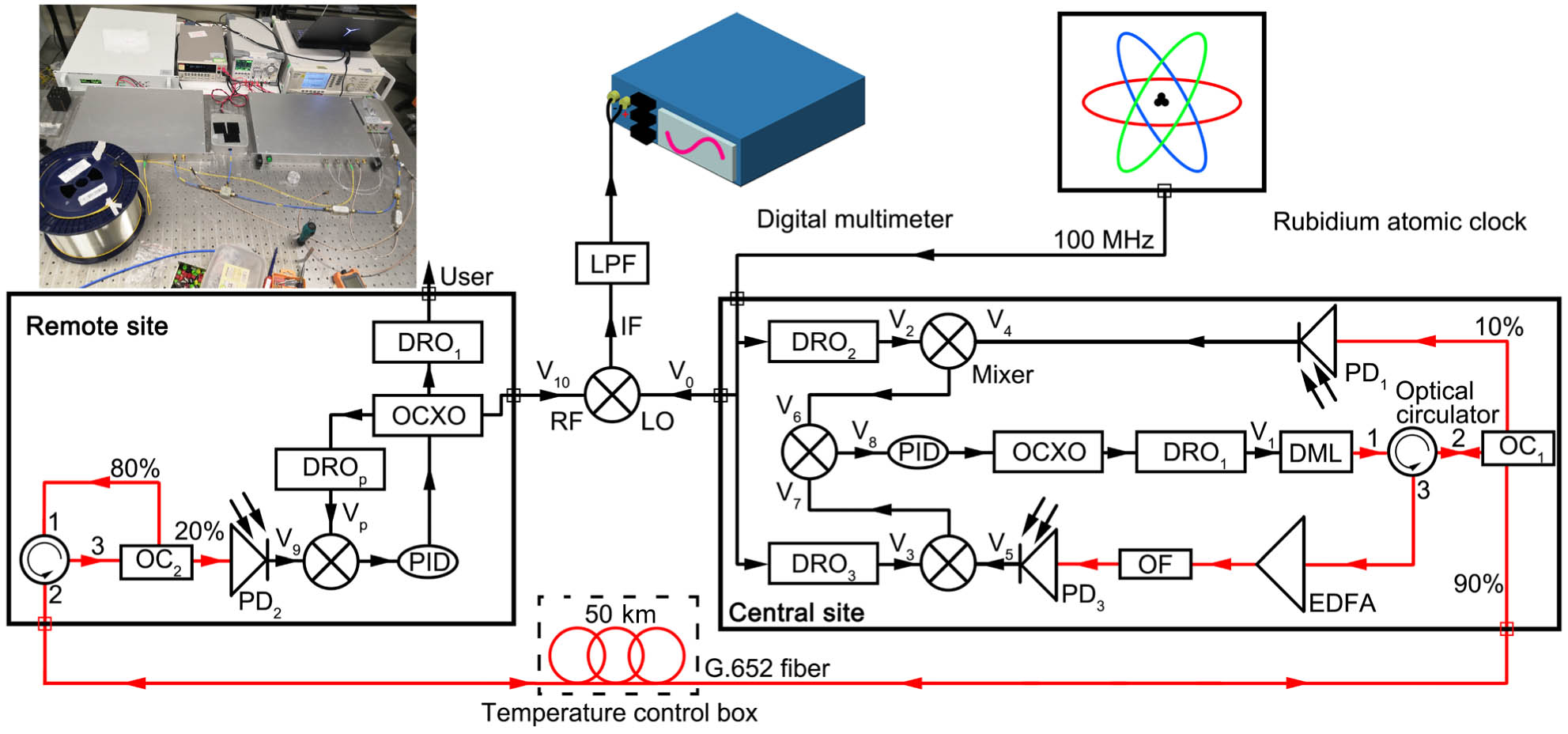
compressed sensing dictionary learning sub-Nyquist radar microwave photonics Doppler frequency The stable long-distance transmission of radio-frequency (RF) signals holds significant importance from various aspects, including the comparison of optical frequency standards, remote monitoring and control, scientific research and experiments, and RF spectrum management. We demonstrate a scheme where an ultrastable frequency signal was transmitted over a 50 km coiled fiber. The optical RF signal is generated using a two-section distributed feedback (DFB) laser for direct modulation based on the reconstruction equivalent chirp (REC) technique. The 3-dB modulation bandwidth of the two-section DFB laser is 18 GHz and the residual phase noise of
frequency dissemination two-section DFB laser phase stability 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦