2019, 17(9) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第17卷 第9期
Ultraviolet (UV) detectors with large photosensitive areas are more advantageous in low-level UV detection applications. In this Letter, high-performance 4H-SiC p-i-n avalanche photodiodes (APDs) with large active area (800 μm diameter) are reported. With the optimized epitaxial structure and device fabrication process, a high multiplication gain of 1.4 × 106 is obtained for the devices at room temperature, and the dark current is as low as ~10 pA at low reverse voltages. In addition, record external quantum efficiency of 85.5% at 274 nm is achieved, which is the highest value for the reported SiC APDs. Furthermore, the rejection ratio of UV to visible light reaches about 104. The excellent performance of our devices indicates a tremendous improvement for large-area SiC APD-based UV detectors. Finally, the UV imaging performance of our fabricated 4H-SiC p-i-n APDs is also demonstrated for system-level applications.
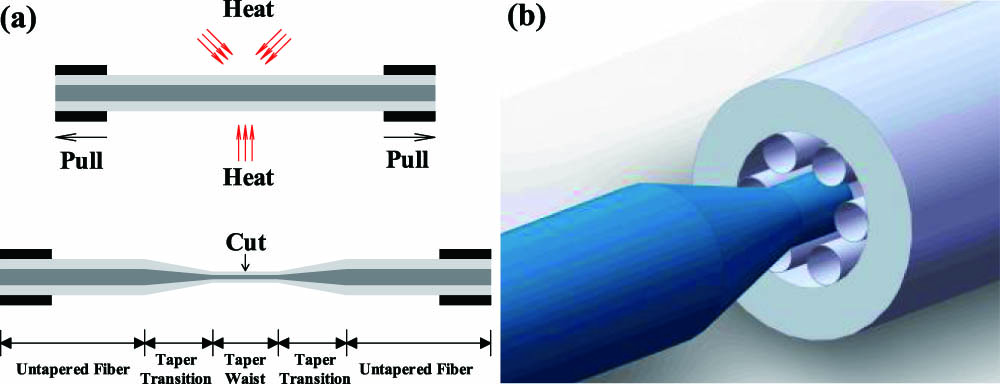
040.1345 Avalanche photodiodes (APDs) 040.7190 Ultraviolet 040.6070 Solid state detectors 230.5160 Photodetectors We have demonstrated a mode matching method between two different fibers by a hybrid thermal expanded core technique, which can be applied to match the modes of fiber-based Fabry–Pérot cavities. Experimentally, this method has achieved an expansion of the ultraviolet fiber core by 3.5 times while keeping fundamental mode propagation. With the experiment parameters, the fundamental mode coupling efficiency between the fiber and micro-cavity can reach 95% for a plano-concave cavity with a length of 400 μm. This method can not only have potential in quantum photonics research but also can be applied in classical optical fields.
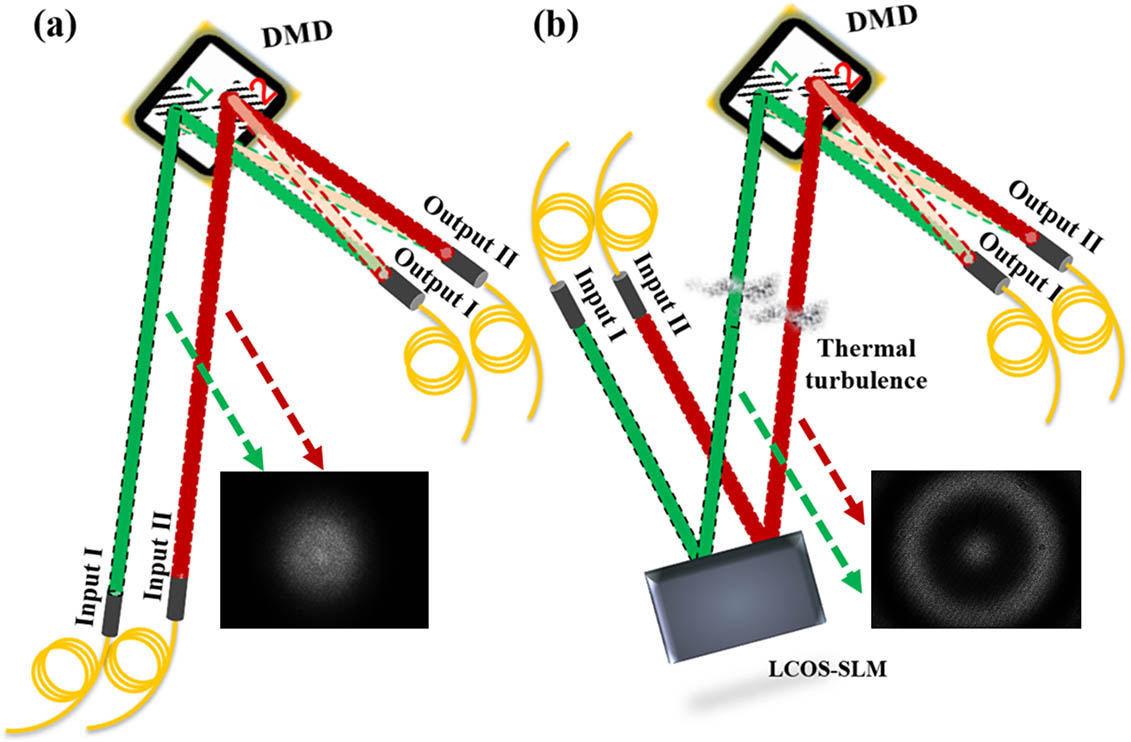
060.2310 Fiber optics 120.2230 Fabry-Perot 140.3948 Microcavity devices 020.5580 Quantum electrodynamics The digital micro-mirror device (DMD)-based optical switch has the advantages of high-speed channels reallocation, miniaturization, stability, and large capacity for short reach optical communication in the datacenter. However, thermal turbulent atmosphere in the datacenter would cause perturbations and channel crosstalk for the optical switch. The self-healing optical beams such as the Bessel beams have the non-diffraction property to mitigate the turbulence issue. Here, we propose and demonstrate a Bessel beams enabled DMD-based optical switch to improve the stability and performance of optical communication in turbulent atmosphere. We statistically characterize the beam wanders of the Gaussian and Bessel beams in turbulent atmosphere at temperatures of 60°C and 80°C. We build the two-channel optical switch communication system and measure the bit error rate of the 15 Gbit/s on–off keying signals transmitted by the Gaussian and Bessel beams at temperatures of 60°C and 80°C, respectively. The optical switch using the Bessel beams shows lower bit error rates with weaker fluctuations compared with the Gaussian beams. The DMD-based optical switch using the Bessel beams has the potential for practical optical communication applications in the datacenter.
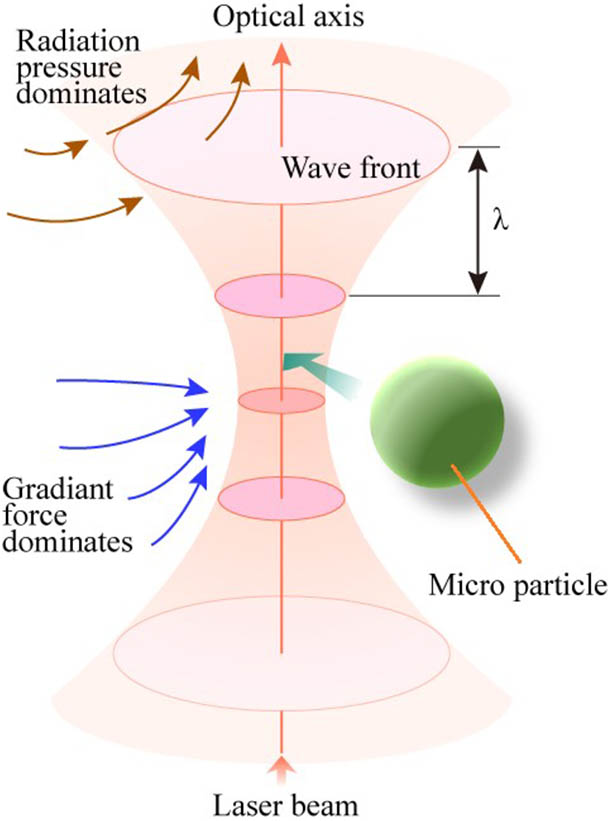
060.4510 Optical communications 130.4815 Optical switching devices 280.7060 Turbulence By using a specialty optical fiber, a series of powerful microparticle manipulation tools, including optical tweezers, a micro-optical hand, and an optical gun, are developed and demonstrated. In this paper, a review of our research activities on the optical manipulation of microparticles is presented. In particular, we will describe a kind of specialty optical fiber designed and fabricated for building optical trapping and manipulating tools. The performances of annular core fiber-based optical tweezers, a multicore fiber-based micro-optical hand, and a coaxial dual waveguide fiber-based optical gun are demonstrated as examples of applications and discussed in detail. The fiber can be used in cell manipulation in life science and drug response in medicine.
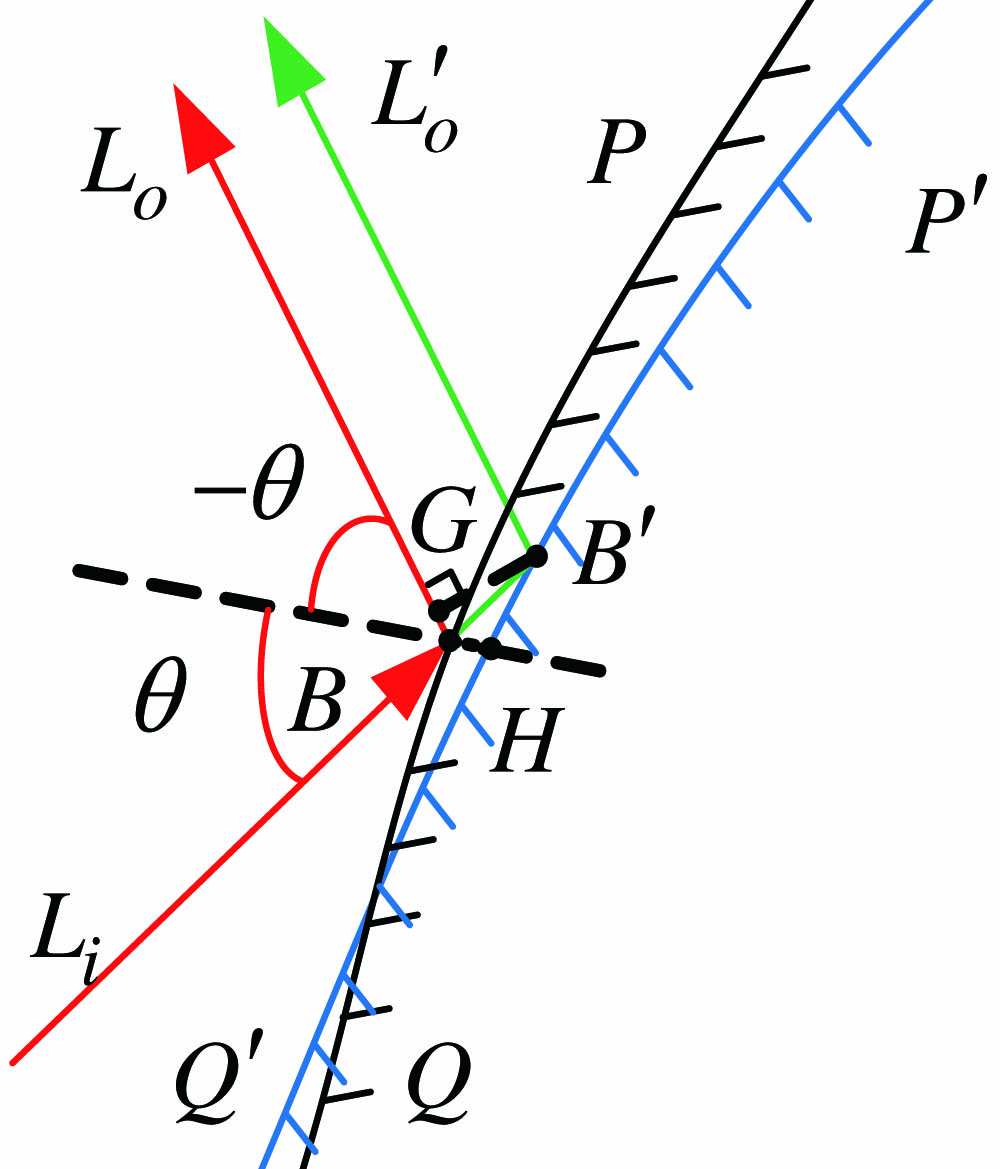
060.2310 Fiber optics 350.4855 Optical tweezers or optical manipulation 140.7010 Laser trapping The misalignment of optical vortex (OV) beams, including transversal displacement and tilt, occurs in many situations, including on reflection or refraction at an interface between two different media and in propagation and tracking systems for optical communications. We propose a reliable method to determine and subsequently eliminate tilt and transversal displacement in an OV beam. An experimental setup was established to verify the proposed method, and the experimental results showed good agreement with those of the numerical simulations. Using the measured misalignments, the initial orbital angular momentum spectrum can be recovered in free space.
060.4510 Optical communications 050.4865 Optical vortices Random Bragg-gratings-based narrow linewidth random fiber laser with a  Download:770次
Download:770次
 Download:770次
Download:770次A new structure of short-cavity random fiber laser (RFL) with narrow linewidth lasing is proposed. A
060.3735 Fiber Bragg gratings 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors A novel see-through virtual retina display (VRD) system is proposed in this Letter. An optical fiber projector is used as the thin-light-beam source, which is modified from a laser scan projector by separating the laser sources and the scan mechanical structure. A synthetic aperture method is proposed for simple, low-cost fabrication of a volume holographic lens with large numerical aperture. These two key performance-enhanced elements are integrated into a lightweight and ordinary-glasses-like optical see-through VRD system. The proposed VRD system achieves a weight of 30 g and a diagonal field of view of 60°.
090.2820 Heads-up displays 090.2890 Holographic optical elements 170.5755 Retina scanning 110.2350 Fiber optics imaging Lensless Wiener–Khinchin telescope based on second-order spatial autocorrelation of thermal light Download:851次
Download:851次
 Download:851次
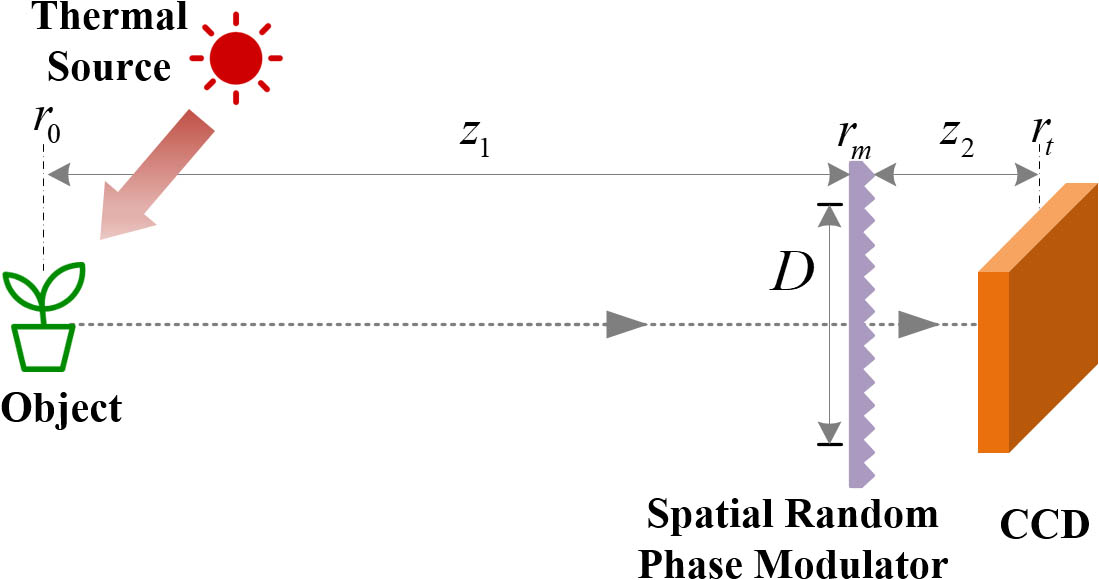
Download:851次The resolution of a conventional imaging system based on first-order field correlation can be directly obtained from the optical transfer function. However, it is challenging to determine the resolution of an imaging system through random media, including imaging through scattering media and imaging through randomly inhomogeneous media, since the point-to-point correspondence between the object and the image plane in these systems cannot be established by the first-order field correlation anymore. In this Letter, from the perspective of ghost imaging, we demonstrate for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, that the point-to-point correspondence in these imaging systems can be quantitatively recovered from the second-order correlation of light fields, and the imaging capability, such as resolution, of such imaging schemes can thus be derived by analyzing second-order autocorrelation of the optical transfer function. Based on this theoretical analysis, we propose a lensless Wiener–Khinchin telescope based on second-order spatial autocorrelation of thermal light, which can acquire the image of an object by a snapshot via using a spatial random phase modulator. As an incoherent imaging approach illuminated by thermal light, the lensless Wiener–Khinchin telescope can be applied in many fields such as X-ray astronomical observations.
110.1758 Computational imaging 110.6150 Speckle imaging 350.1260 Astronomical optics 290.5825 Scattering theory Absolute cryogenic radiometer for high accuracy optical radiant power measurement in a wide spectral range Download:843次
Download:843次
 Download:843次
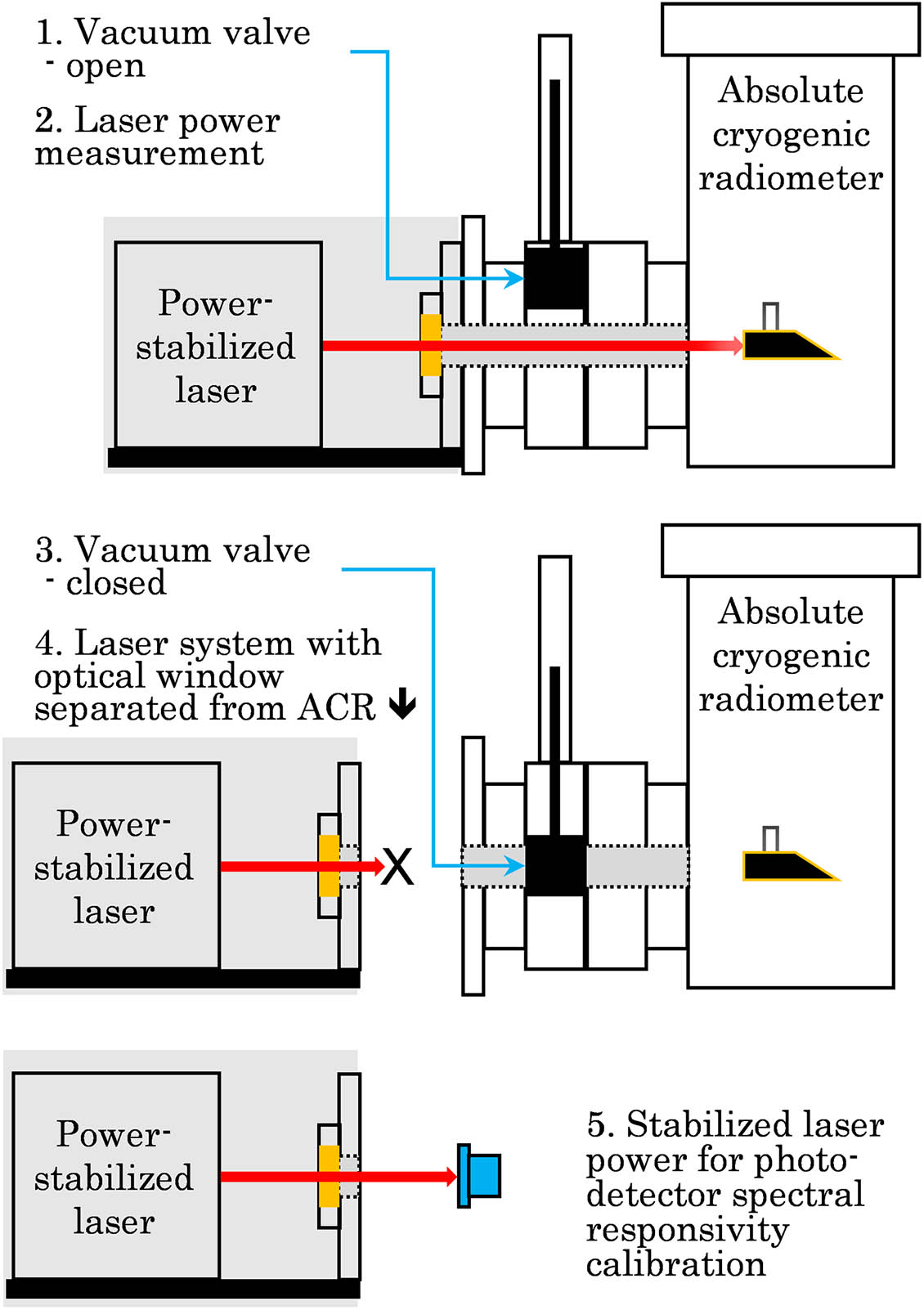
Download:843次An absolute cryogenic radiometer (ACR) with a detachable optical window was designed and built for high accuracy optical radiant power measurement and photodetector spectral responsivity calibration. The ACR receiver is an electroplated pure copper cavity with a 50-μm-thick wall and inner surface coated with a specular black polymer material mixed with highly dispersible carbon nanotubes. The absorptivity of the cavity receivers was evaluated to be ≥0.9999 in the 250 nm–16 μm wavelength range and ≥0.99995 in 500 nm–16 μm. The cavity receiver works at the temperature of ~5.2 K with nanowatt-level noise-equivalent power. The relative standard uncertainty is 0.041% for the measurement of ~100 μW optical radiant power (250 nm–16 μm) and 0.015% for ~1 mW (500 nm–16 μm).
120.3930 Metrological instrumentation 120.3940 Metrology 120.5630 Radiometry Large-scale absolute distance measurement with dual free-running all-polarization-maintaining femtosecond fiber lasers Download:1108次
Download:1108次
 Download:1108次
Download:1108次We demonstrate a robust femtosecond LIDAR setup by using two free-running environmentally stable all-polarization-maintaining nonlinear amplified loop mirror mode-locked fiber lasers. Based on the asynchronous optical sampling method, a ranging accuracy of ±2 μm within 65 m has been achieved, as tested in an 80-m-long underground optical tunnel. Through the Kalman filter in real-time data processing, the measurement accuracy can be maintained at a 200 Hz update rate. This setup provides a practical tool for various large-scale industrial and astronomical ranging applications.
120.0120 Instrumentation, measurement, and metrology 140.4050 Mode-locked lasers 320.7090 Ultrafast lasers Dual-wavelength synchronously mode-locked Tm-doped bulk laser with terahertz frequency beating Download:857次
Download:857次
 Download:857次
Download:857次A dual-wavelength synchronously mode-locked homogeneously broadened bulk laser operating at 1985.6 and 1989 nm is presented for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, which delivers a maximum output power of 166 mW and a repetition rate of 85 MHz. The pulse duration was measured to be 16.8 ps by assuming a
140.4050 Mode-locked lasers 140.3580 Lasers, solid-state 140.3070 Infrared and far-infrared lasers We report here on a diode-pumped pulsed mid-infrared laser source based on gas-filled hollow-core fibers (HCFs) towards an all-fiber structure by the tapering method. The pump laser is coupled into an acetylene-filled HCF through a tapered single-mode fiber. By precisely tuning the wavelength of the diode to match different absorption lines of acetylene near 1.5 μm, mid-infrared emission around 3.1–3.2 μm is generated. With 2 m HCFs and 3 mbar acetylene gas, a maximum average power of 130 mW is obtained with a laser slope efficiency of ~24%. This work provides a potential scheme for all-fiber mid-infrared fiber gas lasers.
140.3070 Infrared and far-infrared lasers 140.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.4130 Molecular gas lasers Yb3+/Er3+ co-doped Na5Lu9F32 single crystals used as a spectral up-converter to improve the power conversion efficiency of perovskite solar cells are prepared via an improved Bridgman approach. Green and red up-conversion (UC) emissions under the excitation of near-infrared (NIR) bands of 900–1000 nm and 1400–1600 nm can be observed. The effectiveness of the prepared materials as a spectral converter is verified by the enhancement of power conversion efficiency of perovskite solar cells. The sample with a UC layer is 15.5% more efficient in converting sunlight to electricity compared to the UC layer-free sample due to the absorption of sunlight in the NIR range. The results suggest the synthesized Yb3+/Er3+ co-doped Na5Lu9F32 single crystals are suitable for enhancing the performance of perovskite solar cells.
160.4670 Optical materials 260.1180 Crystal optics 260.2510 Fluorescence 350.6050 Solar energy In this study, the feasibility of visualization of human joints using photoacoustic tomography (PAT) is investigated. To verify this idea, the system of integrated optical fiber bundles and a custom-made flexible transducer is established, both of which give the advantage of morphological adaptation; therefore, the coupling section can be worn on human limbs. The imaging capacity of the flexible-transducer-based PAT system is validated by mapping the structures of the finger and the wrist joint. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first time to achieve photoacoustic imaging of such large human wrist joints. The cross-sectional photoacoustic images of a healthy joint clearly exhibit the main internal structures, including the phalanx, tendons, and blood vessels, which are comparable with the corresponding images by 3.0 T magnetic resonance imaging. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed system holds promise for early diagnosis of joint disorders.
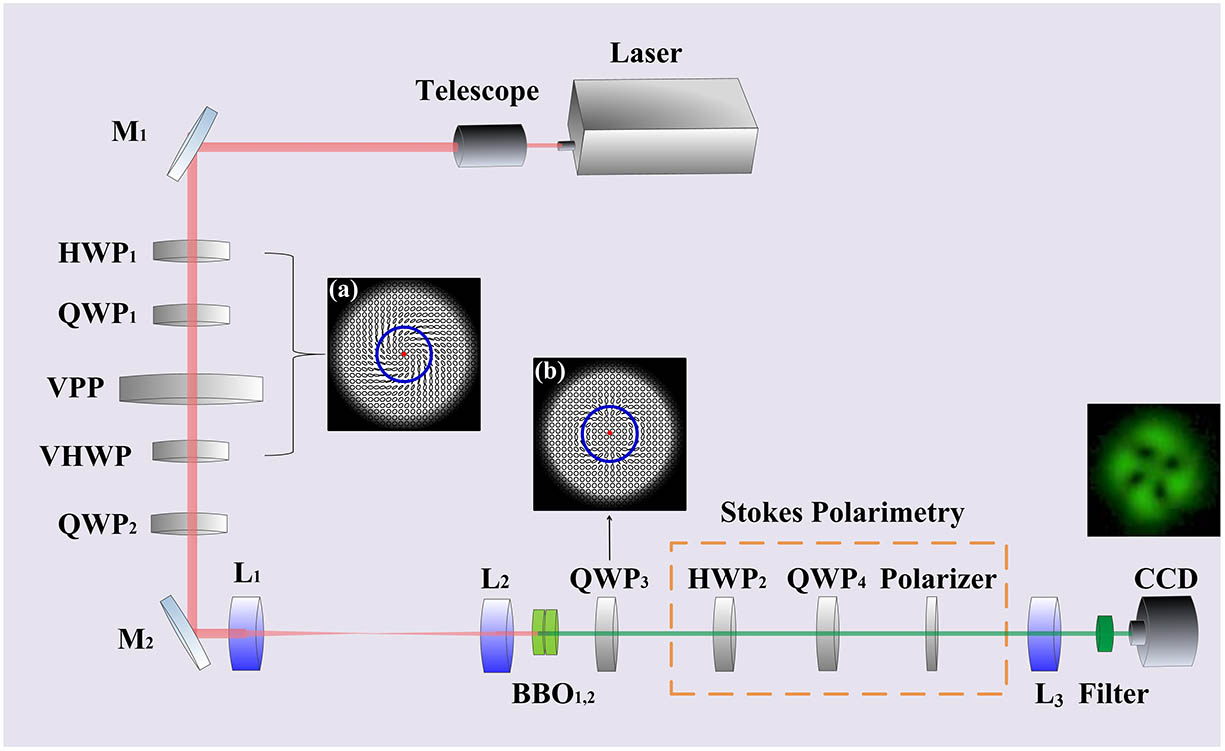
170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging 170.3880 Medical and biological imaging We demonstrate the full vectorial feature of second-harmonic generation (SHG), i.e., from infrared full Poincaré beams to visible full Poincaré beams, based on two cascading type I phase-matching beta barium borate crystals of orthogonal optical axes. We visualize the structured features of the vectorial SHG wave by using Stokes polarimetry and show the interesting doubling effect of the polarization topological index, i.e., a low-order full Poincaré beam is converted to a high-order one. However, the polarization singularities of both C points and L lines are found to keep invariant during the SHG process. Our scheme could offer a deeper understanding on the interaction of vectorial light fields with media and can be generalized to other nonlinear optical effects.
190.2620 Harmonic generation and mixing 260.6042 Singular optics Design method for freeform reflective-imaging systems with low surface-figure-error sensitivity Download:873次
Download:873次
 Download:873次
Download:873次Freeform surfaces are difficult to manufacture due to their lack of rotational symmetry. To reduce the requirements for manufacturing precision, a design method is proposed for freeform reflective-imaging systems with low surface-figure-error sensitivity. The method considers both the surface-figure-error sensitivity and optical specifications, which can design initial systems insensitive to surface figure errors. Design starts with an initial planar system; the surface-figure-error sensitivity of the system is reduced during construction. The proposed method and another that is irrelevant to figure-error sensitivity are used to design a freeform off-axis three-mirror imaging system. Comparison of the sensitivities of the two systems indicates the superiority of our proposed method.
220.4830 Systems design 080.4228 Nonspherical mirror surfaces 220.4610 Optical fabrication 080.4035 Mirror system design A scanning three-dimensional coherent laser radar (ladar) based on the frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) is proposed and demonstrated, which can obtain many three-dimensional high-quality images. The system utilizes an electro-optic modulator and an optical filter to output a linear FMCW with a bandwidth of 2 GHz. The flexible and variable rotating double prism is used for beam scanning. The images of flight demonstration are formed by attitude compensation correction. The experiment result validates the performance of our system for airborne three-dimensional scanning imaging.
280.3400 Laser range finder 280.3640 Lidar 100.6890 Three-dimensional image processing 040.2840 Heterodyne An experimental investigation of two-color polarization spectroscopy (TCPS) is presented based on the cesium 6S1/2 – 6P3/2 – 8S1/2 (852.3 nm + 794.6 nm) ladder-type system in a room-temperature vapor cell. The dependency of line shapes of TCPS on the power of a 852.3 nm pump and a 794.6 nm probe laser is measured in detail, and we confirm that the linewidth of TCPS in a counter-propagating configuration between the pump and probe laser beams is obviously narrower than that of a co-propagating configuration, due to the atomic coherence effect. It is helpful for laser stabilization of the excited state transition using TCPS without frequency modulation.
300.6210 Spectroscopy, atomic 020.1670 Coherent optical effects 020.3690 Line shapes and shifts 300.3700 Linewidth A reflecting-type highly efficient terahertz cross-polarization converter based on metamaterials Download:836次
Download:836次
 Download:836次
Download:836次We propose and experimentally demonstrate a wideband linear polarization converter in a reflection mode operating from 2.4 to 4.2 THz with conversion efficiency of more than 80%. Our device can expand the applications to a higher frequency band. A numerical simulation is performed for this metamaterial converter, which shows a good agreement with experimental results. Importantly, a concise and intuitive calculating model is proposed for the Fabry–Pérot cavity. The theoretical results indicate that the underlying reason for the enhanced polarization conversion is the additional phase difference induced by the resonance of the meta-structure and multiple reflections within the Fabry–Pérot cavity.
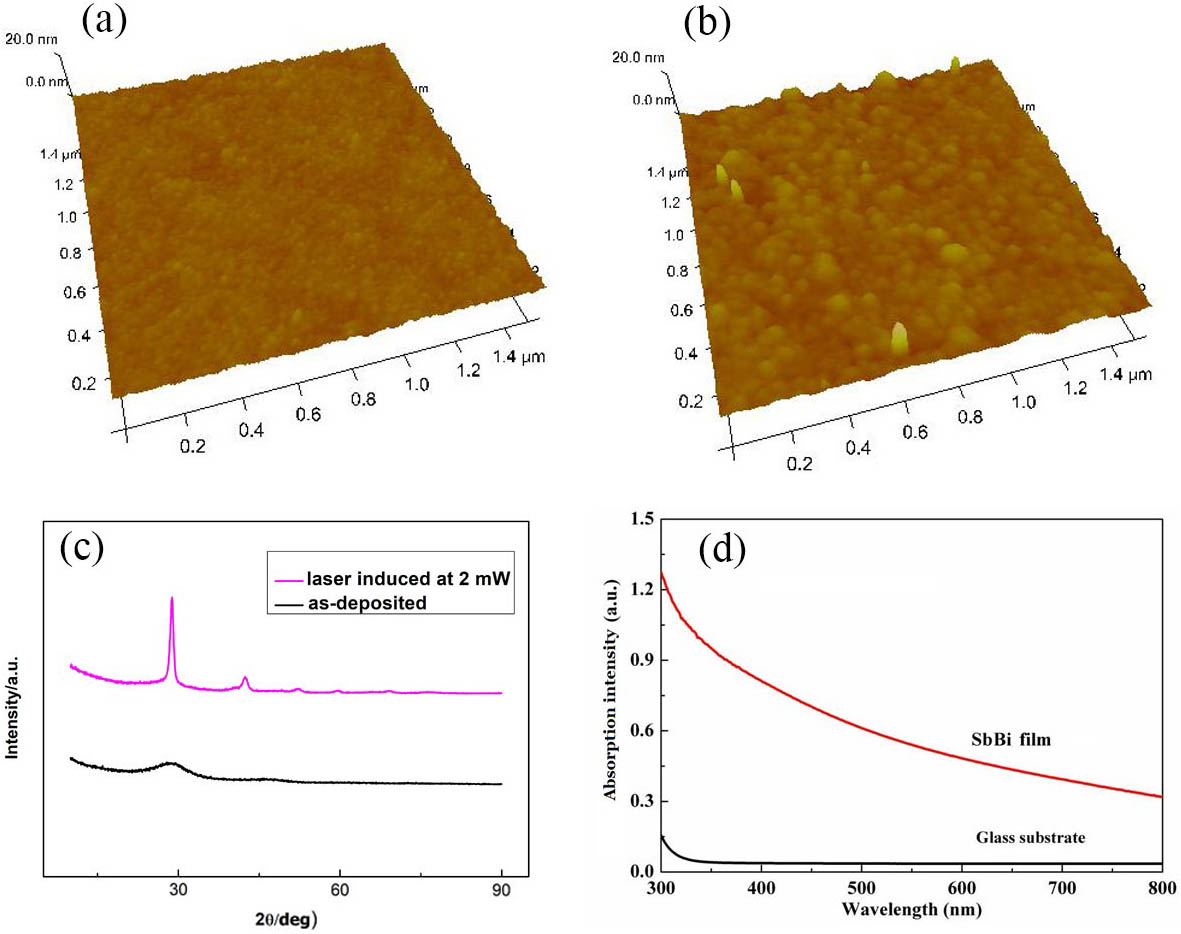
310.5448 Polarization, other optical properties 310.6628 Subwavelength structures,nanostructures 310.6805 Theory and design 240.5445 Polarization-selective devices A Te-free binary phase change material SbBi is proposed as a new inorganic photoresist for heat-mode lithography. It shows good film-forming ability (surface roughness <1 nm), low threshold power for crystallization (2 mW), and high etching selectivity (15:1). Line-type, dot-type, and complex pattern structures with the smallest feature size of 275 nm are fabricated on SbBi thin films using a 405 nm diode laser direct writing system. In addition, the excellent grating structures with a period of 0.8 μm demonstrate that thermal interference does not affect the adjacent microstructures obviously. These results indicate that SbBi is a promising laser heat-mode resist material for micro/nanostructure fabrication.
310.6845 Thin film devices and applications 140.3380 Laser materials 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦