2016, 14(12) Column
the 50th Anniversary of the Invention of Optical Fiber Communications Diffraction and Gratings Fiber Optics and Optical Communications Holography Imaging Systems Instrumentation, Measurement and Metrology Lasers and Laser Optics Machine Vision Materials Nonlinear Optics Physical Optics Quantum Optics Remote Sensing and Sensors Spectroscopy Ultrafast Optics X-Ray Optics
Chinese Optics Letters 第14卷 第12期
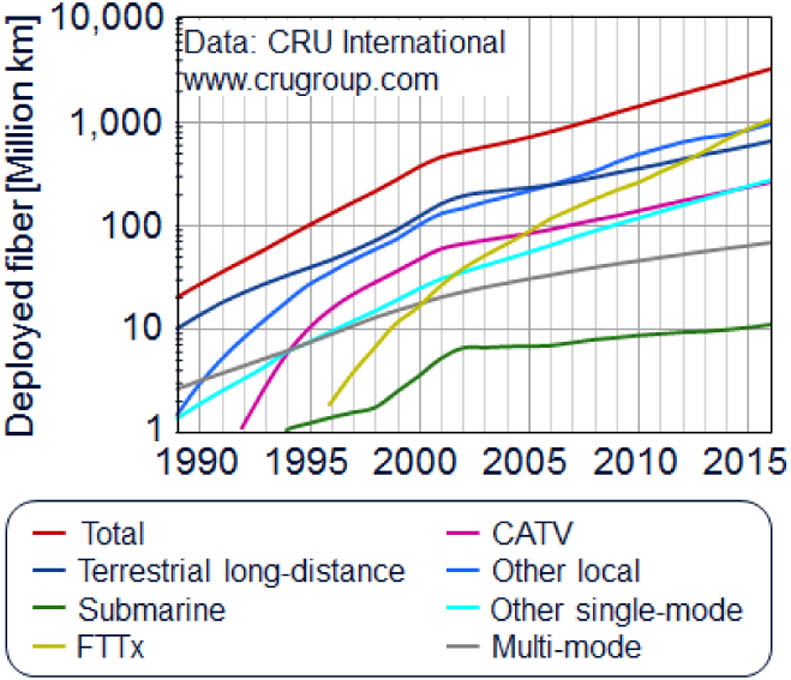
This Review focuses on optical transmission fibers and the high-capacity systems operating thereon. It attempts to combine key lessons learned from the 50-year history of low-loss optical fibers with views on future fiber and systems requirements, discussing likely evolution paths and potential pitfalls in resolving the optical network capacity crunch.
060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications From 2010 to 2015, the Wuhan Institute of Posts and Telecommunications (WRI) had undertaken the national key basic research development program project ‘ultra-high speed, ultra-large capacity, ultra-long distance (3U) optical transmission based research’ as the leading agency. Under the support of the project, we have obtained a series of achievements in scientific research and engineering. Some of the results have been widely used in commercial systems. This Review will make a preliminary summary of the achievements during the past 5 years.
060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications 250.0250 Optoelectronics 070.0070 Fourier optics and signal processing We review the research and development of beyond Pb/s capacity space-division-multiplexed transmission technology using multi-core optical fibers for satisfying the ever-increasing traffic demand. Moreover, we present an optical packet and circuit integrated network technology to improve switching capacity and flexibility in network nodes for the rapid traffic fluctuation and the data service diversification.
060.1660 Coherent communications 060.2330 Fiber optics communications 060.4510 Optical communications The advent of low loss optical fiber has consistently led us to the ultra-broadband era, where bandwidths exceeding 1 Gb/s are commonplace. This Review reviews the early history of fiber access, pointing out some of the lasting design choices and signature features of fiber access. The progress of the various passive optical network technologies is also reviewed, and some views regarding the future trends of fiber in the access.
060.2330 Fiber optics communications 060.4263 Networks, star Distribution of millimeter waves over a fiber link with high frequency stability (Invited Paper) Download:744次
Download:744次
 Download:744次
Download:744次We present a theoretical analysis, systematic simulation, and experimental measurements for the phase noise, timing jitter, and frequency stability in the frequency distribution of millimeter waves over distant optical fiber links. The conception that the dissemination of a higher frequency reference instead of a lower one can achieve a better frequency stability is discussed and verified. We find that the system’s noise floor, including thermal noise, shot noise, and any other noise from electronic components, is considered to be a fundamental limitation for a frequency reference transmission system. Benefiting from the high-precision time delay variation discrimination and accurate locking control operation, a highly stabilized reference is distributed to a remote end over a 60 km spooled fiber, achieving a frequency stability of 4 × 10 17
120.5050 Phase measurement 060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 070.1170 Analog optical signal processing The uses of optical fibers are numerous, and over the past few decades, they have extended from optical fiber communications to a wide variety of sensing applications. In particular, fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensors inscribed in single-mode optical fibers offer significant advantages over more conventional electrical sensors and have been successfully deployed in many different industries. In this Review, we review the applications of intrinsic FBG pressure and flow sensors in oil and gas and the deployment of FBG sensing networks in railways. The promising prospect of using polymer FBGs in wearable medical devices is also described.
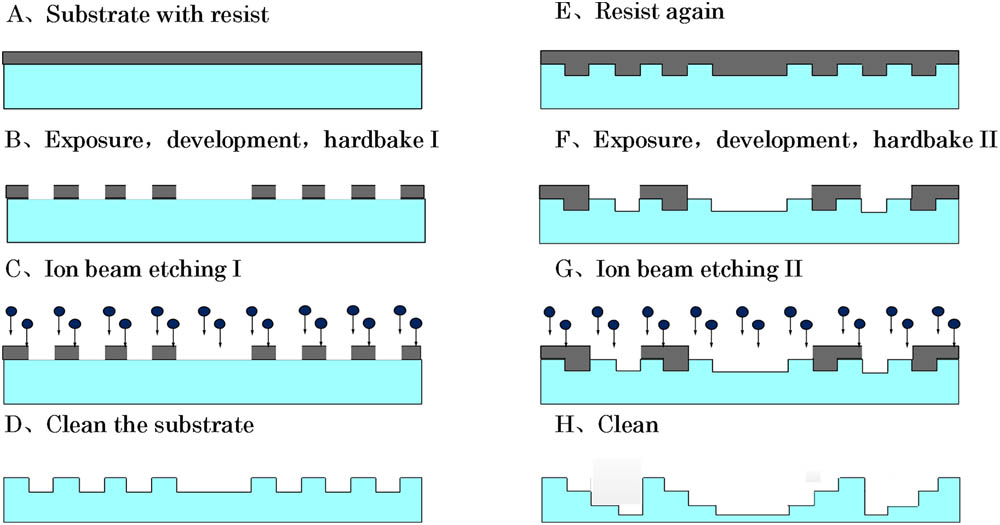
060.3735 Fiber Bragg gratings 280.0280 Remote sensing and sensors 280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors 280.4991 Passive remote sensing The demand for space-borne telescopes with an aperture of 20 m is forcing the development of large diameter diffractive Fresnel zone lenses (FZLs) on membranes. However, due to the fabrication errors of multi-level microstructures, the real diffraction efficiency is always significantly smaller than the theoretical value. In this Letter, the effects of a set of fabrication errors on the diffraction efficiency for a diffractive membrane are studied. In order to verify the proposed models, a 4-level membrane FZL with a diameter of 320 mm is fabricated. The fabrication errors of the membrane FZL are measured, and its diffraction efficiency in the + 1
050.1965 Diffractive lenses 160.5470 Polymers 120.4610 Optical fabrication We present a single-mode multilayer-core fiber with a large mode area (LMA) and a low bending loss in this Letter. A low equivalent core-cladding refractive index difference is achieved by exploiting the multilayer structure. The multilayer structure has a better bending performance than a traditional step-index core and this structure also contributes to realizing different curved refractive index profiles that have a better bending performance. An index trench is also introduced to dramatically reduce the bending loss. The experimental results show that, at a wavelength of 1550 nm, the mode area of the fabricated fiber is about 215.5 μm 2
060.2280 Fiber design and fabrication 060.2310 Fiber optics 060.2400 Fiber properties 060.2430 Fibers, single-mode The bonded distributed feedback (DFB) fiber laser (FL) acoustic emission sensor and the intensity response of the DFB-FL to external acoustic emissions are investigated. The dynamic sensitivity of the DFB-FL is calibrated by a referenced piezoelectric receiver. In the DFB-FL we used here, the minimum detectable signal is 2 × 10 6 m / s
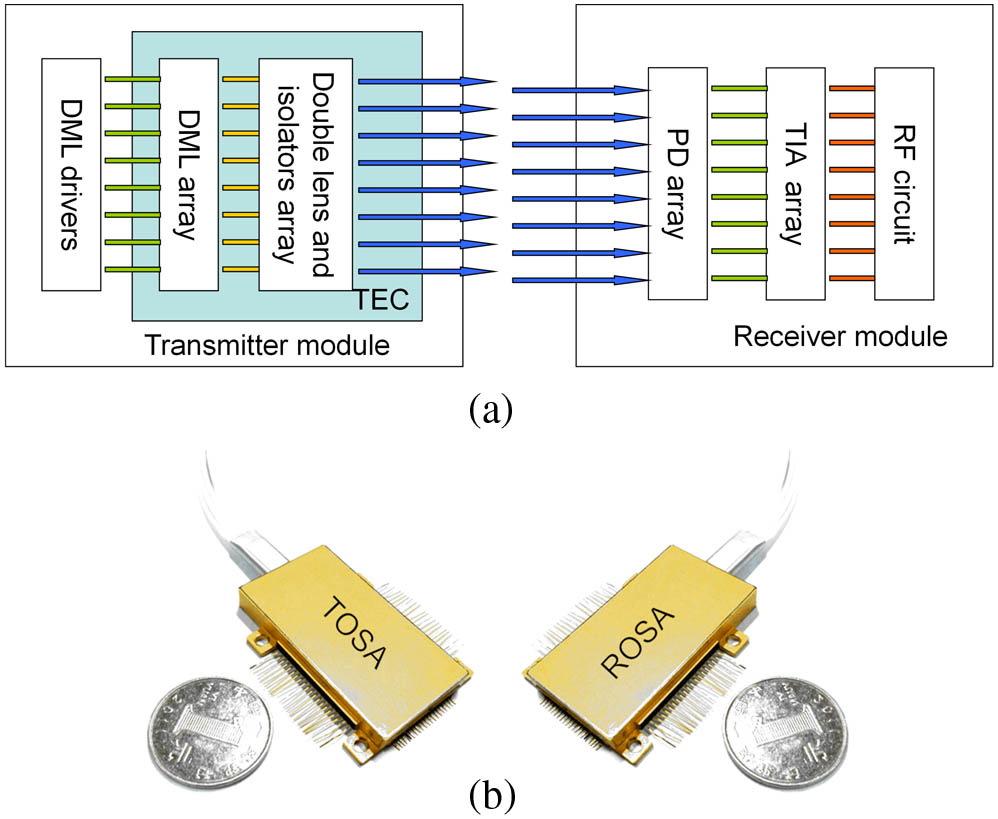
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 140.3490 Lasers, distributed-feedback 140.3510 Lasers, fiber Compact transmitter and receiver optical sub-assemblies (TOSA and ROSA) are fabricated in our laboratory and have an aggregated capacity of 100 Gb/s. Specially, directly modulated laser (DML) drivers with two layers of electrical circuit boards are designed to inject RF signals and bias currents separately. For all the lanes, the 3 dB bandwidth of the cascade of the TOSA and ROSA exceeds 9 GHz, which allows the 12.5 Gb/s operation. With the 12.5 Gb/s × 8-lane operation, clear eye diagrams for back-to-back and 30-km amplified transmission with a dispersion compensation fiber are achieved. Low cost and simple processing technology make it possible to realize commercial production.
060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications 140.0140 Lasers and laser optics 230.0230 Optical devices 250.0250 Optoelectronics We experimentally demonstrate a 750 Mb/s real-time visible light communication (VLC) system based on non-return-to-zero on–off keying modulation by employing single commercially available monochromatic light-emitting diodes. To enhance the 3-dB bandwidth of the VLC link, we propose a low-complexity cascaded post-equalizer based on NPN transistors. With two different frequency-selecting networks in our post-equalizer, the highest achieved 3-dB bandwidth of the VLC link is 370 MHz. The highest achieved data rate is 750 Mb/s at a communication distance of 170 cm with a bit error rate below 1 × 10 6 3.8 × 10 3
060.4510 Optical communications 060.2605 Free-space optical communication 070.4340 Nonlinear optical signal processing 230.3670 Light-emitting diodes The recently proposed random-phase-free method enables holographic reconstructions with very low noise, which allows fine projections without time integration of sub-holograms. Here, we describe the additional advantage of this method, namely, the extended depth of sharp imaging. It can be attributed to a lower effective aperture of the hologram section forming a given image point at the projection screen. We experimentally compare the depth of focus and imaging resolution for various defocusing parameters in the cases of the random-phase method and the random-phase-free method. Moreover, we discuss the influence of the effective aperture in the presence of local obstacles in the hologram’s plane.
090.1705 Color holography 090.1760 Computer holography 090.2870 Holographic display 090.5694 Real-time holography Regeneration of elemental images in integral imaging for occluded objects using a plenoptic camera Download:576次
Download:576次
 Download:576次
Download:576次In this Letter, we propose an elemental image regeneration method of three-dimensional (3D) integral imaging for occluded objects using a plenoptic camera. In conventional occlusion removal techniques, the information of the occlusion layers may be lost. Thus, elemental images have cracked parts, so the visual quality of the reconstructed 3D image is degraded. However, these cracked parts can be interpolated from adjacent elemental images. Therefore, in this Letter, we try to improve the visual quality of reconstructed 3D images by interpolating and regenerating virtual elemental images with adjacent elemental images after removing the occlusion layers. To prove our proposed method, we carry out optical experiments and calculate performance metrics such as the mean square error (MSE) and the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR).
110.0110 Imaging systems 110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition Modeling the encoding structure and spatial resolution of photon counting imagers with Vernier anode readout Download:614次
Download:614次
 Download:614次
Download:614次We present the spatial resolution estimation methods for a photon counting system with a Vernier anode. A limiting resolution model is provided according to discussions of surface encoding structure and quantized noise. The limiting resolution of a Vernier anode is revealed to be significantly higher than that of a microchannel plate. The relationship between the actual spatial resolution and equivalent noise charge of a detector is established by noise analysis and photon position reconstruction. The theoretical results are demonstrated to be in good agreement with the experimental results for a 1.2 mm pitch Vernier anode.
110.3010 Image reconstruction techniques 030.5260 Photon counting 040.7480 X-rays, soft x-rays, extreme ultraviolet (EUV) We employ the in-site automated observation radiometric calibration (AORC) approach to perform vicarious calibration, which does not require the manual efforts of a field team to measure the surface conditions. By using an automated test-site radiometer (ATR), the surface radiance at any moment in time can be obtained. This Letter describes the AORC approach and makes use of data to compute top-of-atmosphere radiance and compare it to measurements from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer. The result shows that the relative deviation is less than 5% and the uncertainty is less than 6.2%, which indicates that the in-site AORC maintains an accuracy level on par with traditional calibration.
120.0280 Remote sensing and sensors 010.0280 Remote sensing and sensors 030.5620 Radiative transfer Revisiting the laser frequency locking method using acousto-optic frequency modulation transfer spectroscopy Download:1122次
Download:1122次
 Download:1122次
Download:1122次We present a laser frequency locking system based on acousto-optic modulation transfer spectroscopy (AOMTS). Theoretical and experimental investigations are carried out to optimize the locking performance mainly from the view of the modulation frequency and index for the specific scheme of AOMTS. An FWHM linewidth of 63 kHz is achieved and the frequency stability in terms of Allan standard deviation reaches 1.4 × 10 12
140.3425 Laser stabilization 140.3518 Lasers, frequency modulated 020.1335 Atom optics 300.6380 Spectroscopy, modulation A 95 W Nd:YAG laser system pumped by a vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) array is described. The laser contains an all-fiber-based seeder, an Nd:YAG regenerative amplifier, and a four-pass amplifier. The laser operates at 300 Hz with energies up to 317 mJ. The beam has a top-hat intensity distribution. The temporal pulse shape is flat in time, and the pulse width can be adjusted in the range of 2–6 ns.
140.3280 Laser amplifiers 140.3295 Laser beam characterization 140.6810 Thermal effects 140.7260 Vertical cavity surface emitting lasers Image registration is an old topic but has a new application in deep-sky imaging fields named live stacking. In this Letter, we propose a live stacking algorithm based on star detection, description, and matching. A thresholding method based on Otsu and centralization is proposed to implement star detection. Then, a translation and rotation invariant descriptor is proposed to provide accurate feature matching. Extensive experiments illustrate that our proposed method is feasible in deep-sky image live stacking.
150.1135 Algorithms 100.4994 Pattern recognition, image transforms 350.1260 Astronomical optics This Letter presents an original technique to design and synthesize an inhomogeneous asymmetrical lens resulting in a special fan-beam radiation pattern in a wide frequency bandwidth. The vertical and horizontal planes of the fan-beam radiation pattern can be determined separately. Wide angle search and detection are achievable by using this type of lens antenna because of its suitable radiation pattern. The proposed relative index profile is validated by the means of commercial CST software and an FDTD scheme.
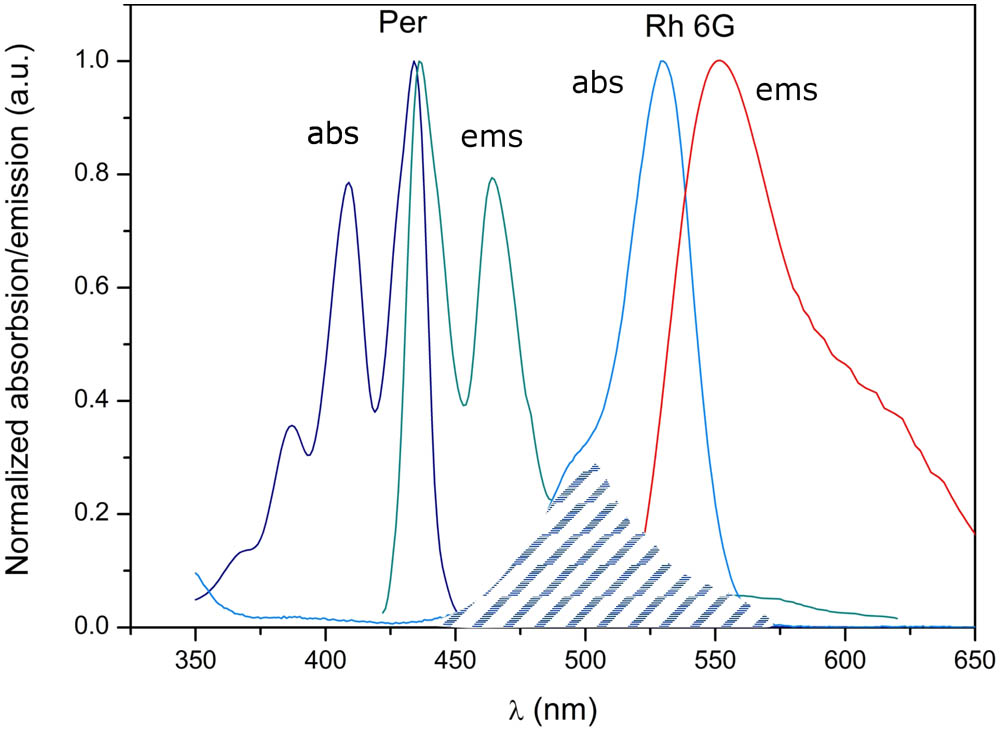
160.3918 Metamaterials 080.0080 Geometric optics 080.3630 Lenses 080.5692 Ray trajectories in inhomogeneous media 110.2760 Gradient-index lenses 230.7370 Waveguides This Letter presents the fabrication and characterization of a perylene (Per) and Rhodamine 6 G (Rh 6 G) co-doped polymeric fiber. The spectroscopic properties (luminescence spectra, attenuation, energy transfer) of the co-doped polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) fiber are presented. Two different concentrations of Rh 6 G (2.2 × 10 4 4.1 × 10 4 mol / L 6.2 × 10 4 mol / L
160.4890 Organic materials 160.2540 Fluorescent and luminescent materials 160.5470 Polymers In this Letter, we report, for the first time to our knowledge, on a continuous-wave, singly resonant optical parametric oscillator using an MgO: PPLN crystal pumped by an all-fiberized master-oscillator power amplifier structured amplified random fiber laser. An idler output power of 2.46 W at 3752 nm is achieved with excellent beam quality, and the corresponding pump-to-idler conversion efficiency is 9.6% at room temperature. The idler output power exhibits a peak-to-peak power stability better than 12.7%, and the corresponding standard deviation is better than 3.6% RMS in about 20 min at the maximum output power. Meanwhile, other characteristics of the generated signal and idler laser are studied in detail and not only offered an effective guide in the research of optical parametric processes in the case of a continuous spectrum, but also broadened the range of random fiber laser applications.
190.4975 Parametric processes 190.4970 Parametric oscillators and amplifiers Electro-optically tunable self-focusing and self-defocusing in KTP crystals by a cascaded second-order process Download:531次
Download:531次
 Download:531次
Download:531次We report the transformation of a linear electro-optically tunable non-phase-matched second-order nonlinear process into a cascaded second-order nonlinear process in a bulk KTP crystal to generate the effect of electro-optically tunable Kerr-type nonlinearity. By applying an electric field on the x – y z
190.2620 Harmonic generation and mixing 190.4360 Nonlinear optics, devices 260.5950 Self-focusing 260.1180 Crystal optics Soliton formation with controllable frequency line spacing using dual pumps in a microresonator Download:695次
Download:695次
 Download:695次
Download:695次Temporal cavity solitons (CSs) have excellent properties that can sustain their shape in a temporal profile and with a broadband, smooth-frequency spectrum. We propose a method for controllable frequency line spacing soliton formation in a microresonator using two continuous-wave (CW) pumps with multi-free-spectral-range (FSR) spacing. The method we propose has better control over the amount and location of the solitons traveling in the cavity compared to the tuning pump method. We also find that by introducing a second pump with frequency N N
190.5530 Pulse propagation and temporal solitons 230.5750 Resonators 190.4410 Nonlinear optics, parametric processes The electron and heavy hole energy levels of two vertically coupled InAs hemispherical quantum dots/wetting layers embedded in a GaAs barrier are calculated numerically. As the radius increases, the electronic energies increase for the small base radii and decrease for the larger ones. The energies decrease as the dot height increases. The intersubband and interband transitions of the system are also studied. For both, a spectral peak position shift to lower energies is seen due to the vertical coupling of dots. The interband transition energy decreases as the dot size increases, decreases for the dot shapes with larger heights, and reaches a minimum for coupled semisphere dots.
190.4720 Optical nonlinearities of condensed matter 160.4760 Optical properties A setup for the generation of arbitrary vector beams is proposed. The setup mainly consists of a spatial light modulator (SLM), an angle-adjustable polarization beam splitter modulator, and a spatial filtering imaging system. Compared with the system using a birefringent beam splitter with a non-adjustable splitting angle, the polarization splitting angle of the improved setup can be adjusted by slightly rotating the related mirrors, which will bring more convenience when different wavelengths and different pixel sizes of SLMs are involved. The experimental results also demonstrate that the setup possesses a good polarization-selective imaging ability, which reveals that the setup may also be useful in polarization-selective spatial filtering imaging and polarization-encoded encryption.
260.5430 Polarization 230.5440 Polarization-selective devices 090.1760 Computer holography A low-noise photodetector is a basic tool for the research of quantum information processing. We present a specially designed low-noise photoelectric detector with a bandwidth of 130 MHz, using a transimpedance amplification circuit. Based on the detailed calculation of the dependence on each parameter of the detector, a useful method of how to design a low-noise and broadband photodetector is provided. When the optical power is between 1.0 and 16 mW, the photodetector has a good linear response to the injected light. Its electronics noise power is below 77 dBm
270.5570 Quantum detectors 270.5585 Quantum information and processing 040.5570 Quantum detectors Short-wave infrared signature and detection of aicraft in flight based on space-borne hyperspectral imagery Download:740次
Download:740次
 Download:740次
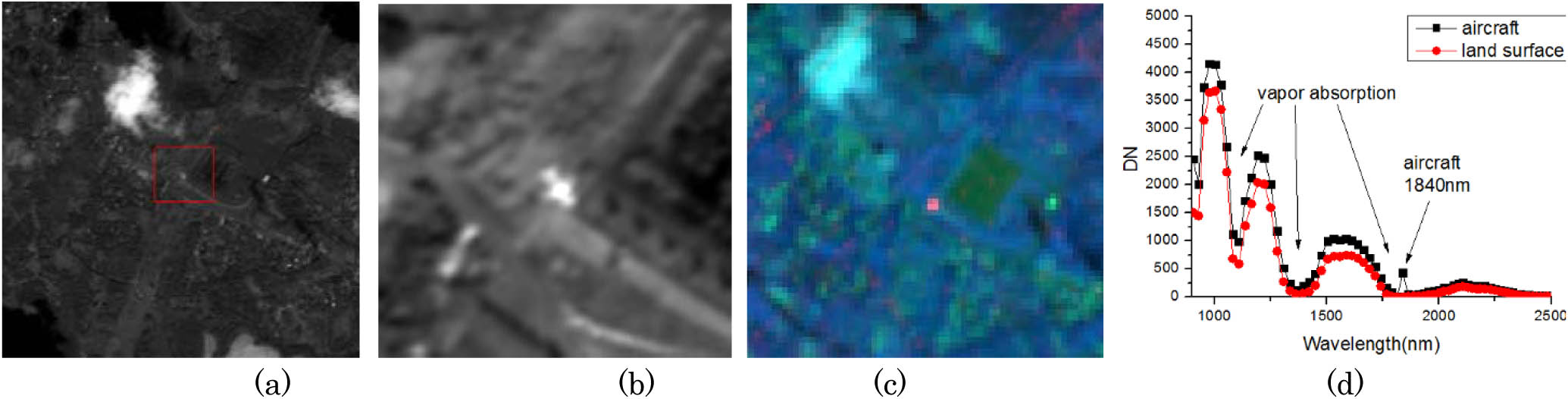
Download:740次Infrared signatures of aircraft are the basis for detection and monitoring. In past years, most of the studies focused on the aircraft’s infrared signature in the mid-wave spectral region and long-wave spectral region for missile guidance or aircraft survivability studies. For the security of civil aviation, methods and instruments that can detect and monitor aircrafts from space are expected to be developed in the coming years. A short-wave infrared hyperspectral imager aboard the Tiangong-1 spacecraft acquired some civil aircraft’s spectral data. The differences between the aircraft and the background in their spectral signatures are analyzed and discussed. Less absorption in the vapor absorption bands and a reflection spike is discovered at the 1.84 μm spectral band. The result shows that 1.84 μm and other vapor absorption bands can make contributions to aircraft detection in the daytime.
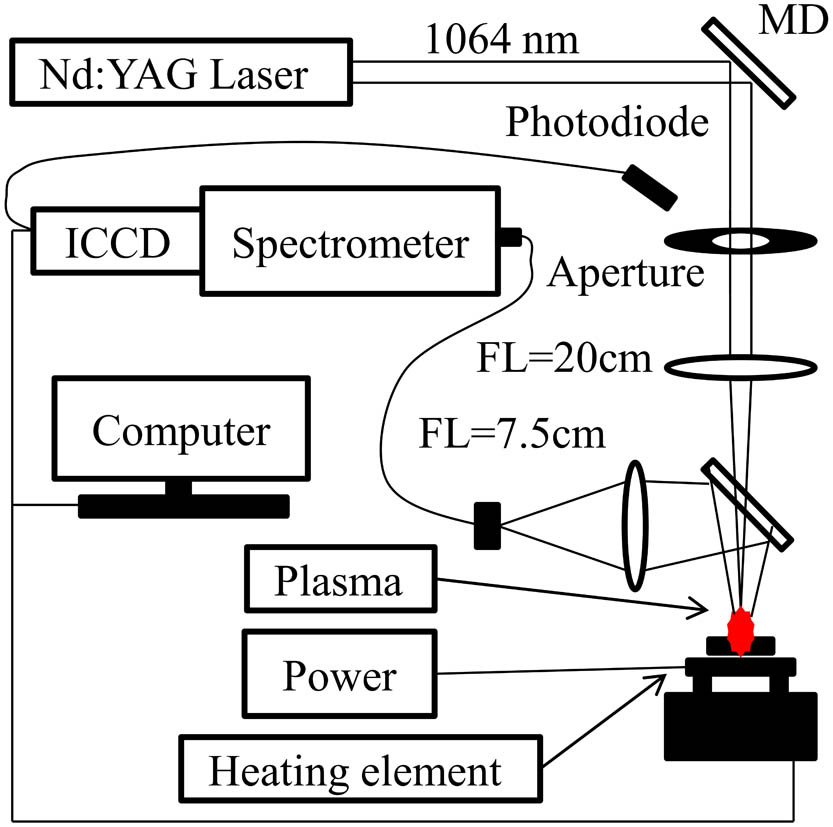
280.4788 Optical sensing and sensors 100.4145 Motion, hyperspectral image processing We investigate the temperature dependence of the emission spectrum of a laser-induced semiconductor (Ge and Si) plasma. The change in spectral intensity with the sample temperature indicates the change of the laser ablation mass. The reflectivity of the target surface is reduced as the sample is heated, which leads to an increase in the laser energy coupled to the surface of the sample and eventually produces a higher spectral intensity. The spectral intensities are enhanced by a few times at high temperatures compared with the cases at low temperatures. The spectral intensity of Ge is enhanced by 1.5 times at 422.66 nm, and 3 times at 589.33 nm when the sample temperature increases from 50°C to 300°C. We can obtain the same emission intensity by a more powerful laser or by less pulse energy with a higher sample temperature. Based on experimental observations we conclude that the preheated sample can improve the emission intensity of laser-induced semiconductor plasma spectroscopy.
300.6365 Spectroscopy, laser induced breakdown 350.5400 Plasmas A background removal method based on two-dimensional notch filtering in the frequency domain for polarization interference imaging spectrometers (PIISs) is implemented. According to the relationship between the spatial domain and the frequency domain, the notch filter is designed with several parameters of PIISs, and the interferogram without a background is obtained. Both the simulated and the experimental results demonstrate that the background removal method is feasible and robust with a high processing speed. In addition, this method can reduce the noise level of the reconstructed spectrum, and it is insusceptible to a complicated background, compared with the polynomial fitting and empirical mode decomposition (EMD) methods.
300.0300 Spectroscopy 070.0070 Fourier optics and signal processing 110.4234 Multispectral and hyperspectral imaging Chalcogenide photonic crystal fiber for ultraflat mid-infrared supercontinuum generation Download:1155次
Download:1155次
 Download:1155次
Download:1155次In this Letter, we numerically simulate the generation of a 1–15 μm mid-infrared supercontinuum (SC) from a highly nonlinear Ge 11.5 As 24 Se 64.5 Ge 11.5 As 24 Se 64.5 2474 W 1 km 1
320.6629 Supercontinuum generation 000.4430 Numerical approximation and analysis 060.4370 Nonlinear optics, fibers 160.4330 Nonlinear optical materials 260.2030 Dispersion Subwavelength ripple formation on planar and nonplanar surfaces by femtosecond laser scanning Download:655次
Download:655次
 Download:655次
Download:655次The self-formation of periodic subwavelength ripples by linear polarized femtosecond laser scanning planar and non-planar tungsten targets on the employed laser wavelength, scanning speed, and energy fluence are examined systematically. The results show that, for a certain laser wavelength, the scanning conditions have no obvious effect to the morphological features of grating structures in the threshold range of laser fluence. The spatial structured period of gratings can be self-consistently interpreted by recently presented physical model of surface two-plasmon resonance. The subwavelength structures on cylindrical surface would be a good method to realize unique surface functions on complex surface of micro-devices.
320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena 310.6628 Subwavelength structures,nanostructures 220.4000 Microstructure fabrication 350.3390 Laser materials processing Wolter-I-like X ray telescope structure using one conical mirror and one quadric mirror Download:873次
Download:873次
 Download:873次
Download:873次Nested multilayer mirrors are commonly used in X ray telescope structure to increase the collecting area. To balance the difficulty and cost of producing these mirrors, Wolter-I structures are replaced with conical Wolter-I structures, but these can lead to significantly poorer angular resolutions. In this Letter, we consider changing one of the mirror shapes (paraboloid or hyperboloid) of a Wolter-I structure to a conical mirror shape, while the other mirror shape remains a quadric surface-type structure, which can thus ensure the imaging quality. The cone-hyperboloid structure is nested to obtain on-axis angular resolution and off-axis images.
220.2740 Geometric optical design 350.1260 Astronomical optics 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦