2019, 17(6) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第17卷 第6期
Atomic Doppler broadening thermometry (DBT) is potentially an accurate and practical approach for thermodynamic temperature measurement. However, previous reported atomic DBT had a long acquisition time and had only been proved at the triple point of water, 0°C, for the purpose of determination of the Boltzmann constant. This research implemented the cesium atomic DBT for fast room temperature measurement. The Cs133 D1 (6S1/2 → 6p1/2 transition) line was measured by direct laser absorption spectroscopy, and the quantity of thermal-induced linewidth broadening was precisely retrieved by the Voigt profile fitting algorithm. The preliminary results showed the proposed approach had a 4 min single-scan acquisition time and 0.2% reproducibility. It is expected that the atomic DBT could be used as an accurate, chip-scale, and calibration-free temperature sensor and standard.
020.1335 Atom optics 300.6210 Spectroscopy, atomic 120.6780 Temperature Optoelectronic components and subsystems such as optically controlled phased array antennas, distributed radar networks, interferometric optical fiber hydrophones, and high-speed optoelectronic chips demand high-accuracy optical time delay measurement with large measurement range and the capability for single-end and wavelength-dependent measurement. In this paper, the recent advances in the optical time delay measurement of a fiber link with high accuracy are reviewed. The general models of the typical time delay measurement technologies are established with the operational principle analyzed. The performance of these techniques is also discussed.
060.2300 Fiber measurements 120.5050 Phase measurement 280.3400 Laser range finder Bidirectional carrier aggregation in next-generation radio-over-fiber heterogeneous network based on FBMC Download:504次
Download:504次
 Download:504次
Download:504次We have projected and verified a bidirectional intra-/inter-radio-access-technology carrier-aggregation method for a next-generation heterogeneous mobile network supported by filter bank multicarrier (FBMC). Successful transmission of intra/inter-band carrier aggregation between five broadband FBMC signals and three bands 4G long-term-evolution-advanced signal over 50 km single-mode fiber plus 10 m free-space is successfully broadcasted by employing an incoherent light-injection scheme in downlink. In uplink, two intra-bands carrier-aggregated wireless local area network Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers 802.11g signal is carried over the equal distance. High receiver sensitivity, low error vector magnitude, and clear constellation diagrams show successful delivery of different wireless services for different consumers. Therefore, the proposed hybrid system should become a potential solution for a future mobile front-haul network because of its low latency and high capacity.
060.2330 Fiber optics communications 060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 060.4080 Modulation We propose a general guideline on the design of a stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS)-based microwave photonic filter (MPF) using a directly modulated pump. Filter gain profiles and passband ripples with waveform repetition periods of the driving current ranging from 2 to 100 ns are measured after the transmission of different fiber lengths. The results show that the filter performance has nothing to do with the fiber length, and the digital-to-analog converter bandwidth requirement for the driving current is no more than 500 MHz. Therefore, the low cost, flexible reconfiguration, and miniaturization characteristics make an SBS filter using a directly modulated pump a promising choice as an MPF.
060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 290.5900 Scattering, stimulated Brillouin 060.2330 Fiber optics communications 060.4080 Modulation Three-dimensional position measurement of a levitated nanoparticle in a vacuum by a Dove prism Download:788次
Download:788次
 Download:788次
Download:788次Forward-scattering-light interferometry has become the most commonly used position detection scheme in optical levitation systems. Usually, three-set detectors are required to obtain the three-dimensional motion information. Here, we simplify the three-set detectors to one set by inserting a Dove prism. We investigate the role of a Dove prism in the position measurement process with an optical levitation system in vacuum. The relationship between the power spectral density and the rotation angle of a Dove prism is experimentally demonstrated and analyzed. This work shows that the Dove prism can greatly reduce the complexity of the experimental setup, which can be applied to compact optical levitation systems for studies in metrology, quantum physics, and biology.
090.1970 Diffractive optics 140.7010 Laser trapping Depth from focus (DFF) is a technique for estimating the depth and three-dimensional (3D) shape of an object from a multi-focus image sequence. At present, focus evaluation algorithms based on DFF technology will always cause inaccuracies in deep map recovery from image focus. There are two main reasons behind this issue. The first is that the window size of the focus evaluation operator has been fixed. Therefore, for some pixels, enough neighbor information cannot be covered in a fixed window and is easily disturbed by noise, which results in distortion of the model. For other pixels, the fixed window is too large, which increases the computational burden. The second is the level of difficulty to get the full focus pixels, even though the focus evaluation calculation in the actual calculation process has been completed. In order to overcome these problems, an adaptive window iteration algorithm is proposed to enhance image focus for accurate depth estimation. This algorithm will automatically adjust the window size based on gray differences in a window that aims to solve the fixed window problem. Besides that, it will also iterate evaluation values to enhance the focus evaluation of each pixel. Comparative analysis of the evaluation indicators and model quality has shown the effectiveness of the proposed adaptive window iteration algorithm.
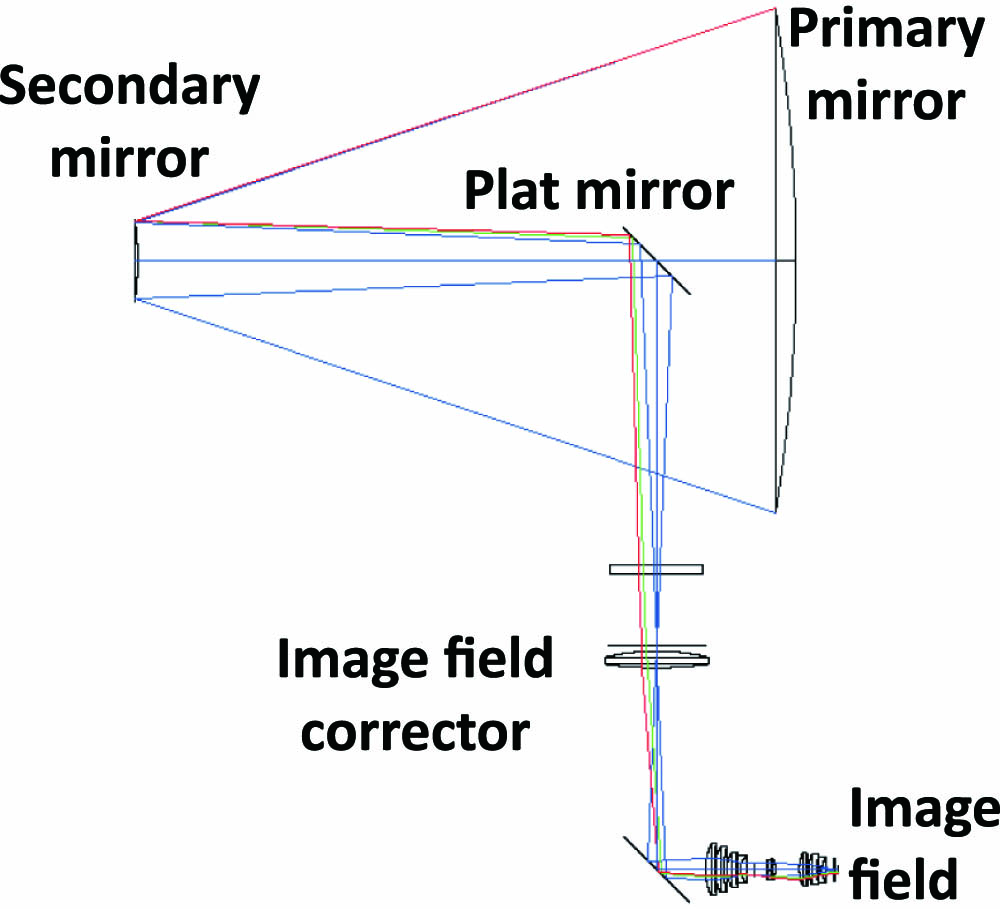
100.6890 Three-dimensional image processing 100.3010 Image reconstruction techniques 100.2980 Image enhancement The precise alignment of a high-performance telescope is a key factor to ensure the imaging quality. However, for telescopes with a wide field of view, the images are sometimes under-sampled. To study the effects of under-sampled images on the precision of telescope alignment, numerical simulations are implemented with the stochastic parallel gradient descent algorithm. The results show that the alignment program can converge stably and quickly. However, with the reduction of the full width at half-maximum of images, the relative residual errors increase from 9.5% to 19.5%, and the wavefront errors raise from 0.0972λ λ
110.6770 Telescopes 120.4820 Optical systems 220.1140 Alignment 220.1080 Active or adoptive optics In this Letter, we reported the preliminary results of an integrating periodically capacitive-loaded traveling wave electrode (CL-TWE) Mach–Zehnder modulator (MZM) based on InP-based multiple quantum well (MQW) optical waveguides. The device configuration mainly includes an optical Mach–Zehnder interferometer, a direct current electrode, two phase electrodes, and a CL-TWE consisting of a U electrode and an I electrode. The modulator was fabricated on a 3 in. InP epitaxial wafer by standard photolithography, inductively coupled plasma dry etching, wet etching, electroplating, etc. Measurement results show that the MZM exhibits a 3 dB electro-optic bandwidth of about 31 GHz, a V π
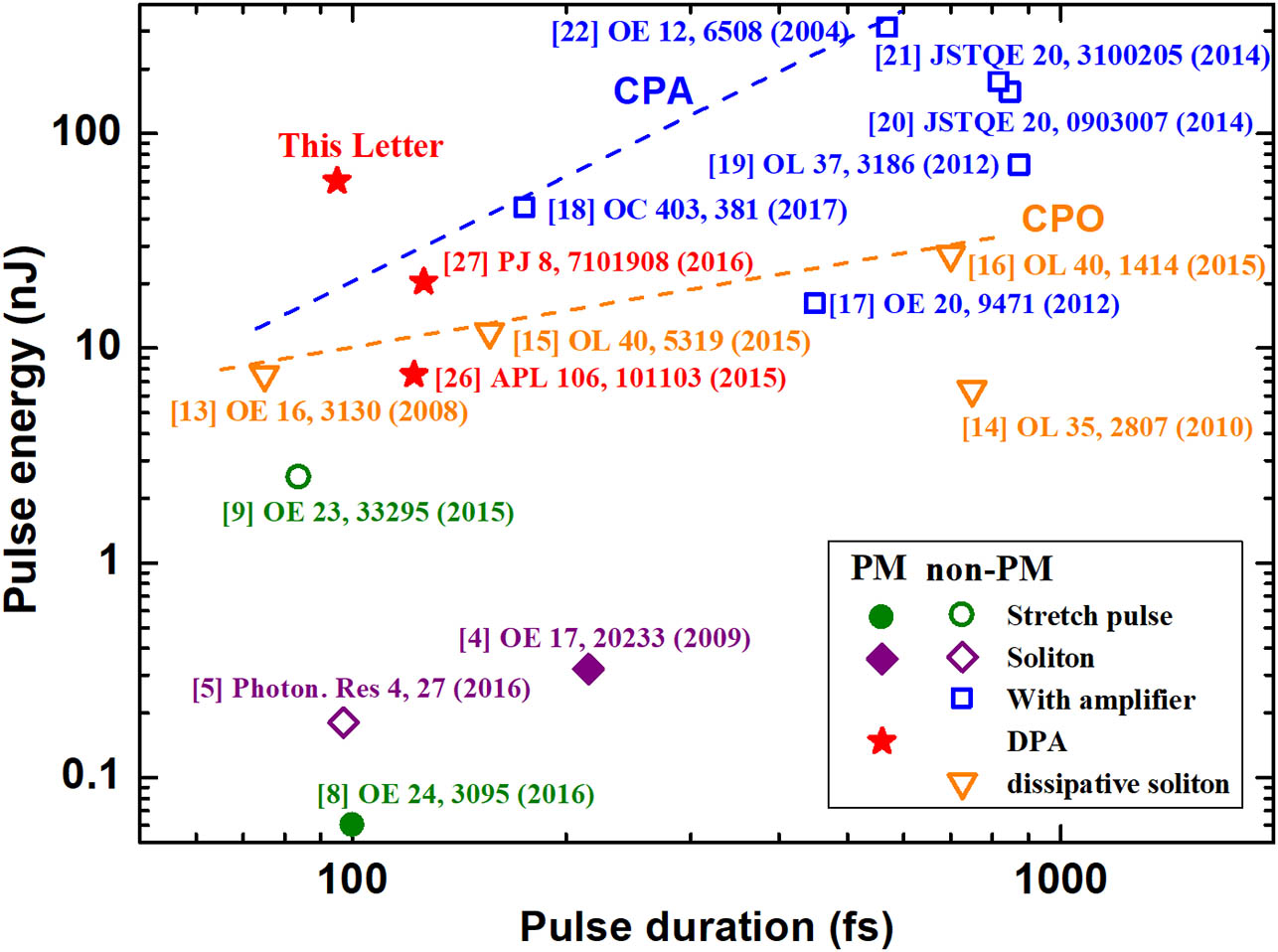
130.3120 Integrated optics devices 250.4110 Modulators 230.4205 Multiple quantum well (MQW) modulators We demonstrate here an environmentally stable and extremely compactable Er-doped fiber laser system capable of delivering sub-100-fs temporal duration and tens of nanojoules at a repetition rate of 10 MHz. This laser source employs a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror mode-locked soliton laser to generate seed pulses. A single-mode-fiber amplifier and a double-cladding-fiber amplifier (both with double-pass configuration) are bridged by a divider and used to manage the dispersion map and boost the soliton pulses. By using 64 replicas, pulses with as high as 60 nJ energy within 95 fs duration are obtained at 10 MHz, corresponding to 600 kW peak power.
140.3500 Lasers, erbium 140.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.4480 Optical amplifiers 140.7090 Ultrafast lasers With tin diselenide (SnSe2) film as a saturable absorber (SA), the passively Q -switched self-frequency doubling (SFD) lasers were realized in Nd3+:ReCa4O(BO3)3 (Re = Y, Gd) crystals. For Nd:YCa4O(BO3)3 crystal, the maximum average output power at 532 nm was 19.6 mW, and the corresponding pulse repetition frequency, pulse duration, single pulse energy, and peak power were 17.6 kHz, 91.9 ns, 1.1 μJ, and 12.1 W, respectively. For Nd:GdCa4O(BO3)3 crystal, these values were 14.5 mW, 22.1 kHz, 48.7 ns, 0.66 μJ, and 13.5 W.
140.3580 Lasers, solid-state 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched 160.4236 Nanomaterials 160.4330 Nonlinear optical materials High power laser diodes (LDs) with a lasing wavelength between 700 and 780 nm have great potential in various medical uses. Here, we report our recent efforts in developing an InGaAsP/AlGaInP-based commercial high power edge-emitting LD, which has 755 nm emission peak with a world-record continuous wave output power of 12.7 W, the highest reported so far. The lack of Al atoms in the active region significantly lowers the chance of catastrophic optical damage during high power laser operation. Meanwhile, with an accumulated 3800 h running time, our ongoing aging tests reveal excellent reliability of our devices.
140.2020 Diode lasers 140.5960 Semiconductor lasers Abnormal elemental redistribution in oxyfluoride glasses induced by high repetition rate femtosecond laser Download:863次
Download:863次
 Download:863次
Download:863次We report on the elemental redistribution behavior in oxyfluoride glasses with a high repetition rate near-infrared femtosecond laser. Elemental analysis by an electro-probe microanalyzer demonstrates that the redistributions of Ca2+ and Yb3+ ions change dramatically with pulse energy, which are quite different compared with previous reported results. Confocal fluorescence spectra of Yb3+ ions demonstrate that the luminescence intensity changes obviously with the elemental redistribution. The mechanism of the observed phenomenon is discussed. This observation may have potential applications in the fabrication of micro-optical devices.
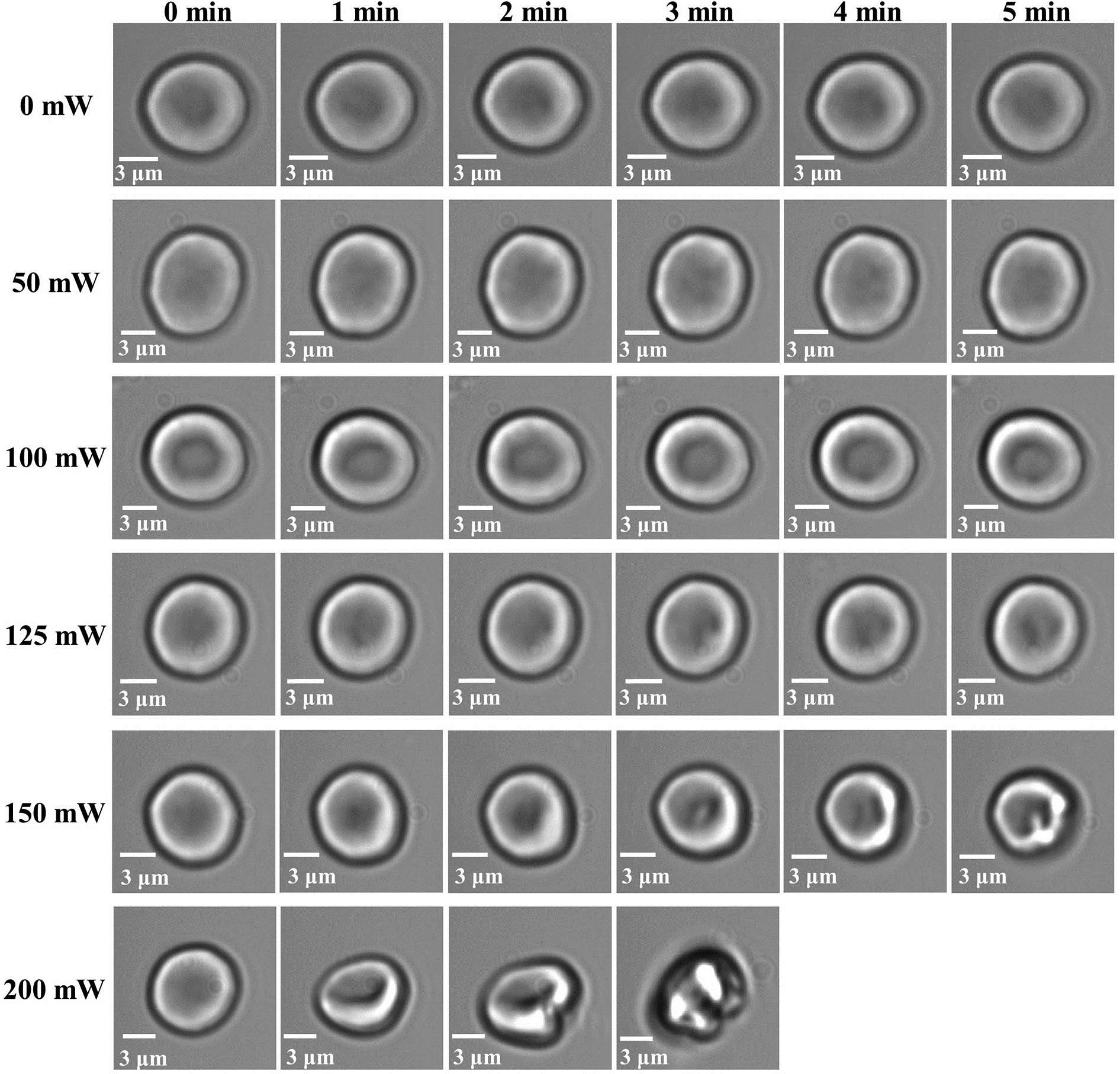
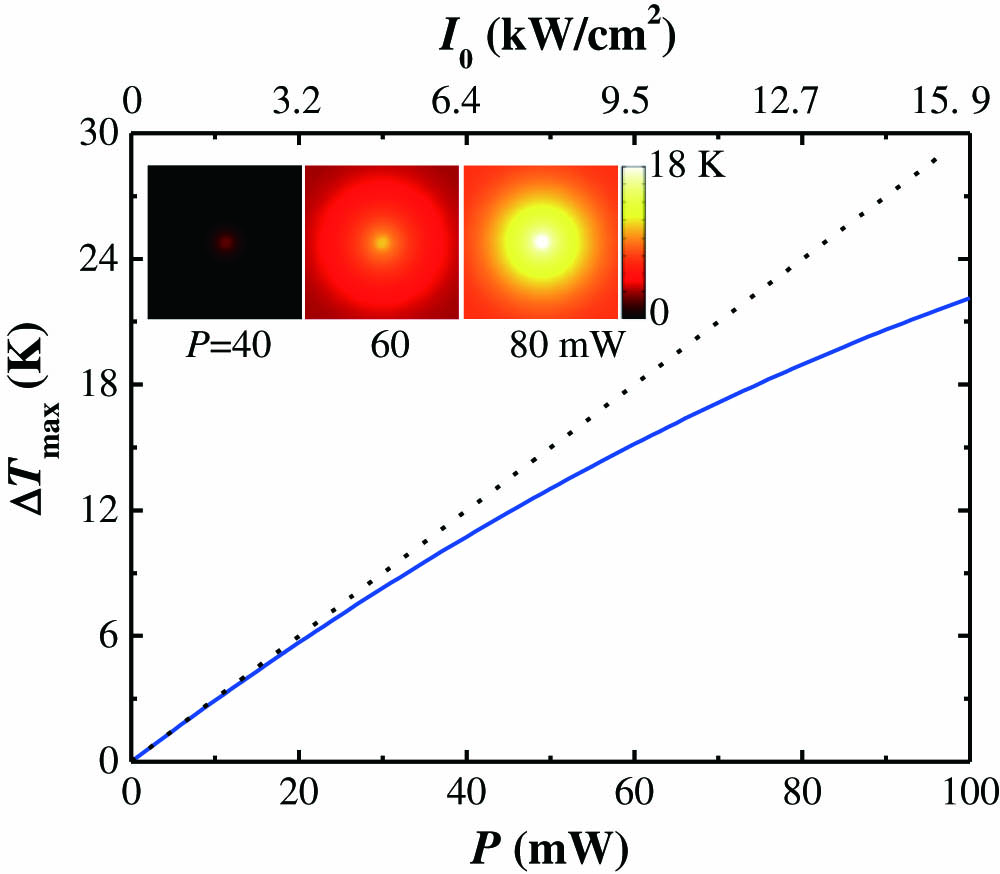
160.5690 Rare-earth-doped materials 160.2750 Glass and other amorphous materials 160.4760 Optical properties 350.3390 Laser materials processing The changes of mechanical properties and biological activities of monomeric erythrocytes are studied using optical tweezers micromanipulation technology. Firstly, the mechanical properties of irradiated erythrocyte membranes are obtained. Weaker power laser irradiation can delay the decay of the mechanical properties of erythrocytes and promote the biological activity of erythrocytes, while higher power laser irradiation damages erythrocytes. The stronger the laser irradiation is, the more obvious and rapid the damage will be. The temperature of the cell surface will be changed by regulating the laser power and irradiation time, so the biological functions of erythrocyte can be controlled. Secondly, the finite element simulation of the temperature change on the cell surface under the condition of laser irradiation is carried out using simulation software, and the precise temperature of the cell surface irradiated cumulatively by a laser with different powers is obtained. Finally, the processes of abscission, unfolding, and denaturation of hemoglobins in erythrocytes at different temperatures due to the photothermal effect are analyzed using the model. The mechanism of laser irradiation on the elasticity of erythrocyte membranes is also obtained.
170.4520 Optical confinement and manipulation 140.6810 Thermal effects 350.4855 Optical tweezers or optical manipulation 350.5340 Photothermal effects Based on natural protein materials, a series of lenses with different heights and focal lengths were assembled on glass substrates by femtosecond laser non-contact, masking, and cold processing. This lens array itself possesses unique and characteristic optical performance in three-dimensional parallel imaging and bending imaging. What is more profound is that by using equilibrium swelling of protein-hydrogel, once the lens array was placed in a liquid environment, with the change of ion concentration (e.g., pH), the refractive index and curvature of the protein-hydrogel would change, which leads to the flex of the focal plane of the lens, finally realizing the dynamical tunability of a protein microlens. These smart stress devices may have great potential in optical biosensing and microfluidic chip integration fields.
170.1420 Biology 230.3990 Micro-optical devices Identification and separation of local and nonlocal optical nonlinear refraction effects: theory and experiment Download:723次
Download:723次
 Download:723次
Download:723次Understanding the nonlinear optical effect of novel materials plays a crucial role in the fields of photonics and optoelectronics. Herein, we theoretically and experimentally investigate the simultaneous presence of third-order locally refractive nonlinearity and thermally induced nonlocal nonlinearity saturation. We present analytical expressions for the closed-aperture Z-scan trace and the number of spatial self-phase modulation (SSPM) rings, which allows one to unambiguously and conveniently separate the contributions of local and nonlocal nonlinear refraction in the case that both effects occur simultaneously. As a test, we study both the local and thermally induced nonlocal nonlinear refraction in fullerene/toluene solution by performing continuous-wave Z-scan and SSPM measurements at two different wavelengths. This work enriches the understanding of the physical mechanism of the optical nonlinear refraction effect in solution dispersions of nanomaterials, which can be exploited for nonlinear photonic devices.
190.4420 Nonlinear optics, transverse effects in 190.4870 Photothermal effects Achromatic Talbot lithography (ATL) with high resolution has been demonstrated to be an excellent technique for large area periodic nano-fabrication. In this work, the uniformity of pattern distribution in ATL was studied in detail. Two ATL transmission masks with ~50% duty cycle in a square lattice were illuminated by a spatial coherent broadband extreme ultraviolet beam with a relative bandwidth of 2.38%. Nonuniform dot size distribution was observed by experiments and finite-difference time-domain simulations. The sum of the two kinds of diffraction patterns, with different lattice directions (45° rotated) and different intensity distributions, results in the final nonuniform pattern distribution.
220.3740 Lithography 220.4241 Nanostructure fabrication Mode couplings of a semiconductor nanowire scanning across a photonic crystal nanocavity Download:723次
Download:723次
 Download:723次
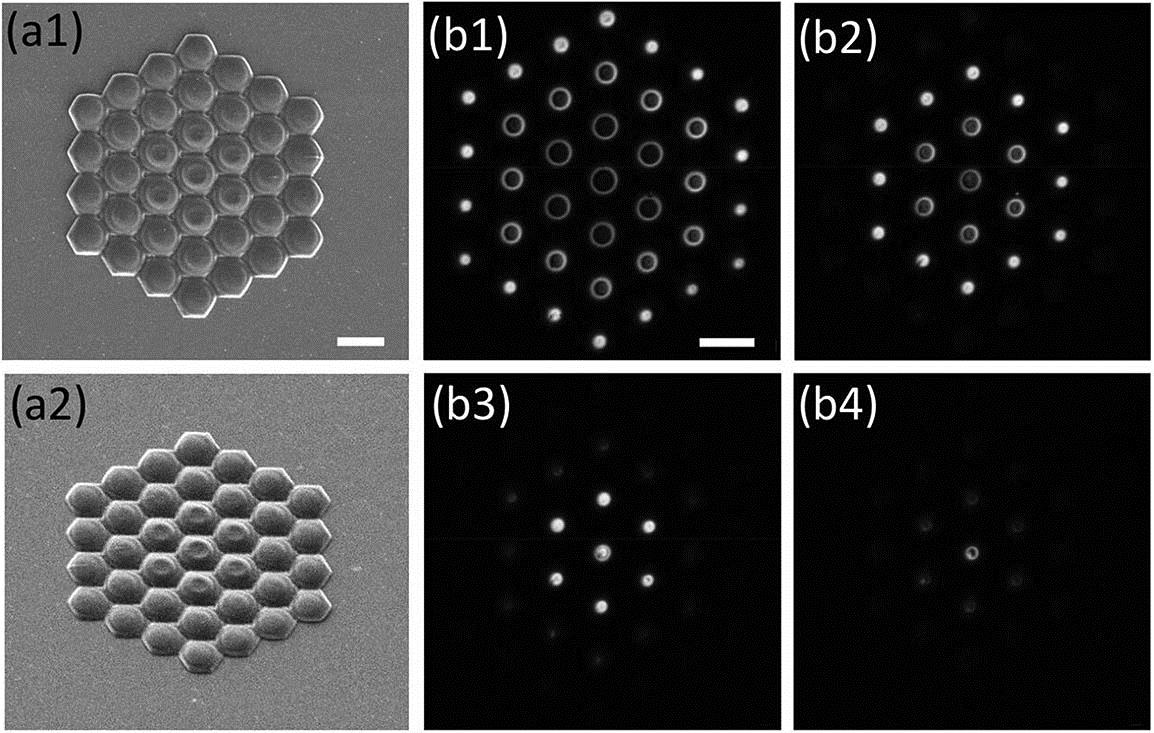
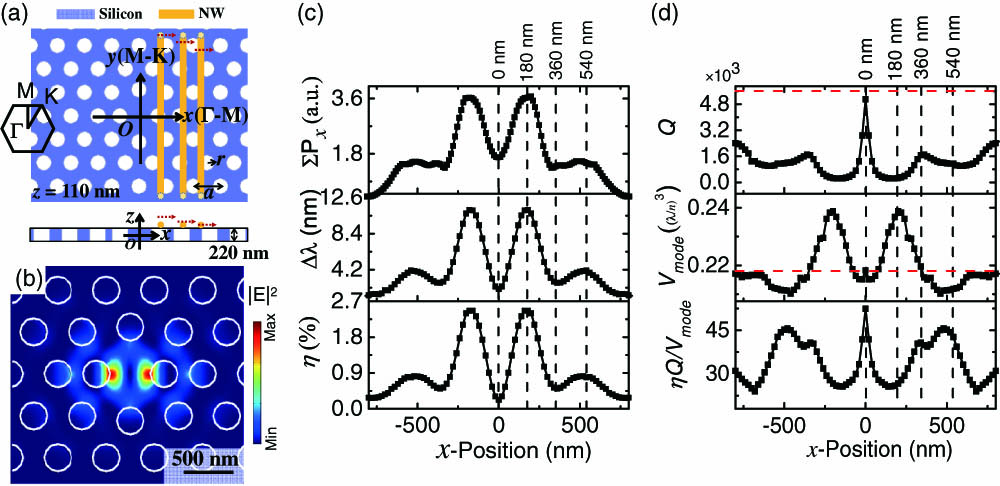
Download:723次The position-dependent mode couplings between a semiconductor nanowire (NW) and a planar photonic crystal (PPC) nanocavity are studied. By scanning an NW across a PPC nanocavity along the hexagonal lattice’s Γ – M and M – K directions, the variations of resonant wavelengths, quality factors, and mode volumes in both fundamental and second-order resonant modes are calculated, implying optimal configurations for strong mode-NW couplings and light-NW interactions. For the fundamental (second-order) resonant mode, scanning an NW along the M – K (Γ – M) direction is preferred, which supports stronger light-NW interactions with larger NW-position tolerances and higher quality factors simultaneously. The simulation results are confirmed experimentally with good agreements.
230.5298 Photonic crystals 160.4236 Nanomaterials 260.5740 Resonance Detecting molecular vibrational modes of side chains and endpoints in nanoscale proteins with graphene plasmon Download:684次
Download:684次
 Download:684次
Download:684次Monitoring the chemical and structural changes in protein side chains and endpoints by infrared (IR) spectroscopy is important for studying the chemical reaction and physical adsorption process of proteins. However, the detection of side chains and endpoints in nanoscale proteins is still challenging due to its weak IR response. Here, by designing a double layered graphene plasmon sensor on MgF2/Si substrate in the IR fingerprint region, we detect the vibrational modes in side chains and endpoints (1397 cm 1 and 1458 cm 1) of monolayer protein. The sensor could be applied on biochemistry to investigate the physical and chemical reaction of biomolecules.
240.6680 Surface plasmons 300.6340 Spectroscopy, infrared 160.4236 Nanomaterials Control amplitude and phase of light by plasmonic meta-hologram with T-shaped nano-cavity Download:782次
Download:782次
 Download:782次
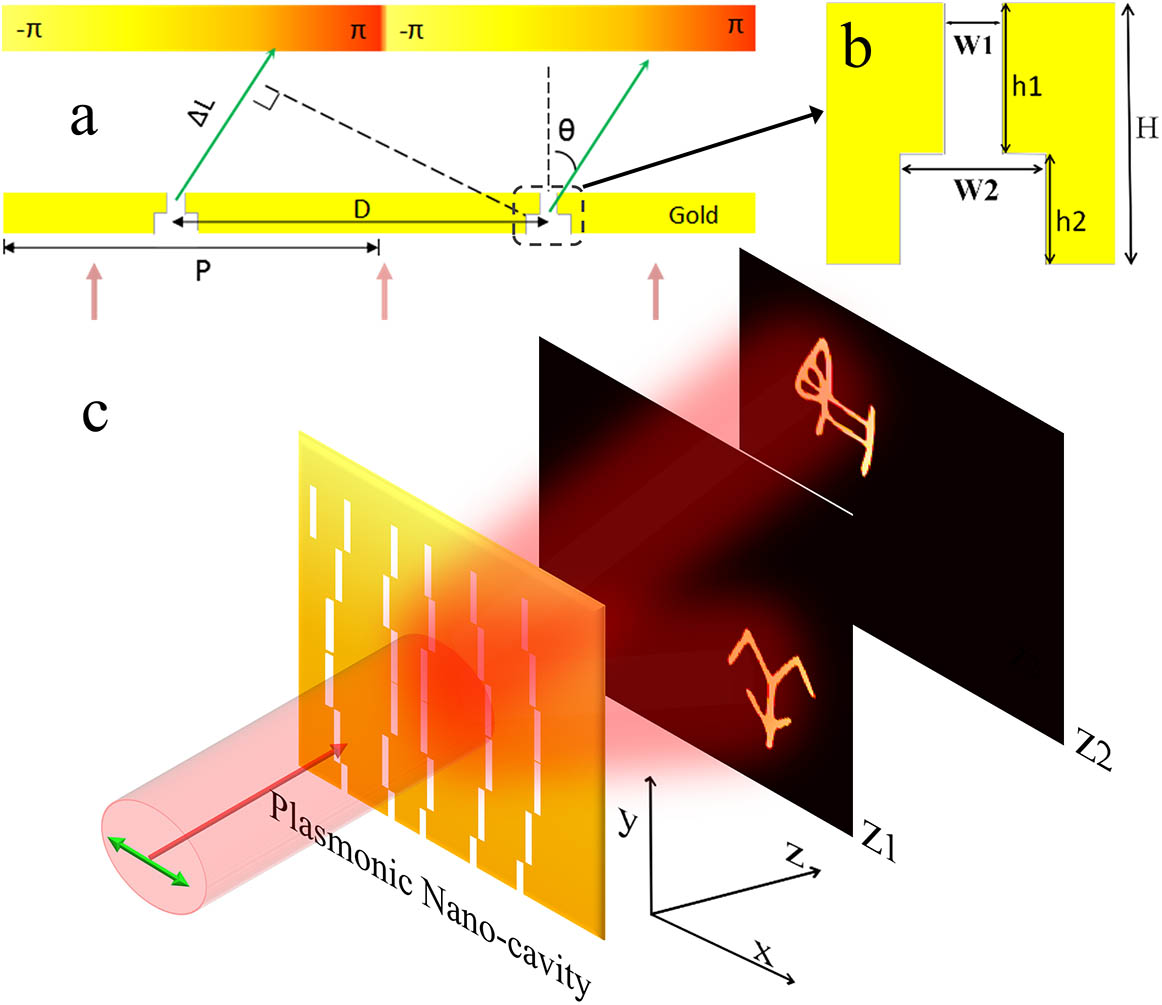
Download:782次Controlling both amplitude and phase of light in the subwavelength scale is a challenge for traditional optical devices. Here, we propose and numerically investigate a novel plasmonic meta-hologram, demonstrating broadband manipulation of both phase and amplitude in the subwavelength scale. In the meta-hologram, phase modulation is achieved by the detour phase distribution of unit cells, and amplitude is continuously modulated by a T-shaped nano-cavity with tunable plasmonic resonance. Compared to phase-only holograms, such a meta-hologram could reconstruct three-dimensional (3D) images with higher signal-to-noise ratio and better image quality, thus offering great potential in applications such as 3D displays, optical communications, and beam shaping.
240.6680 Surface plasmons 160.3918 Metamaterials 090.2890 Holographic optical elements 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦